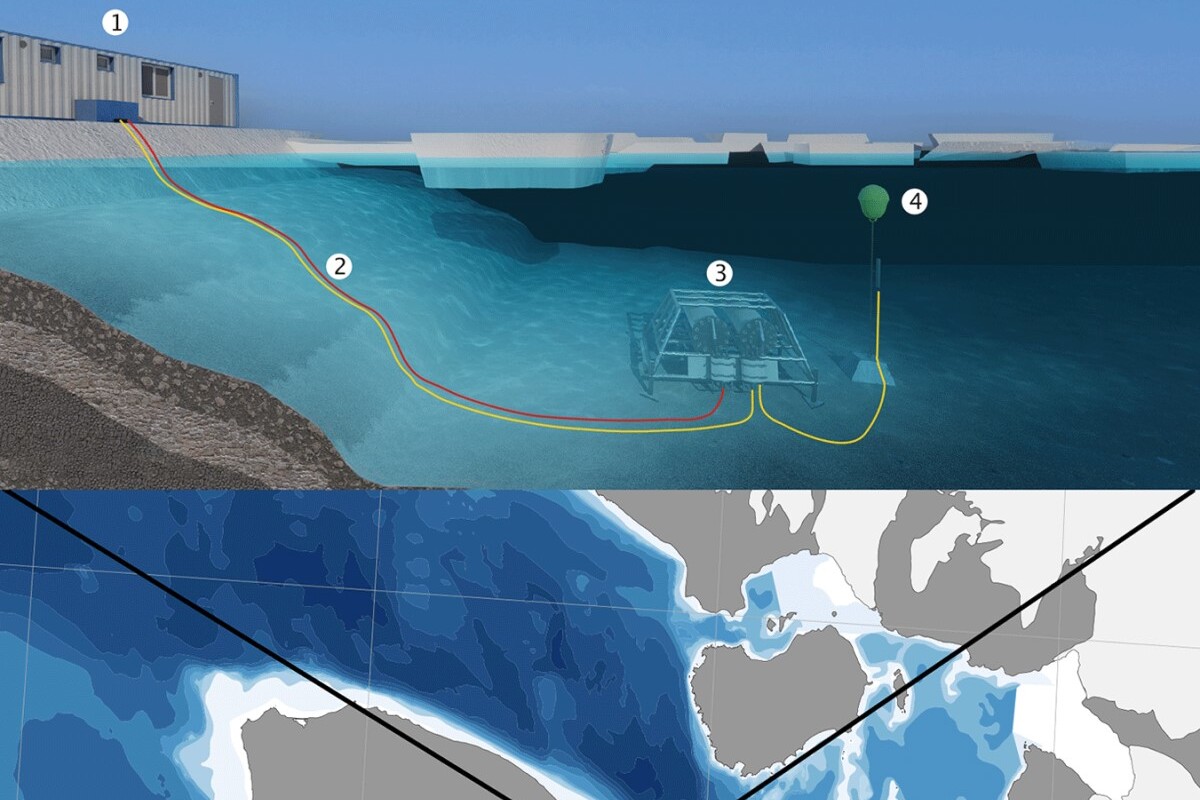
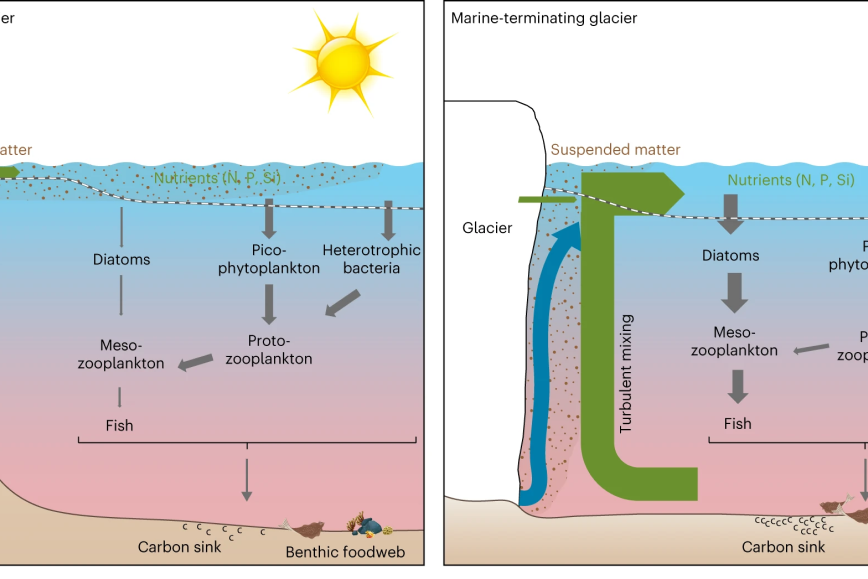
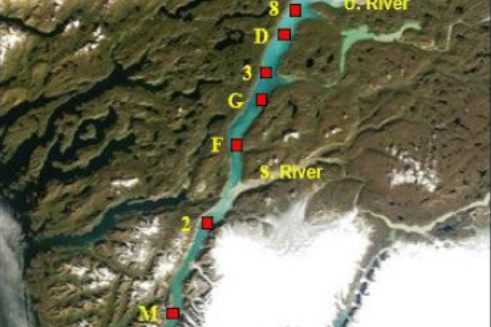
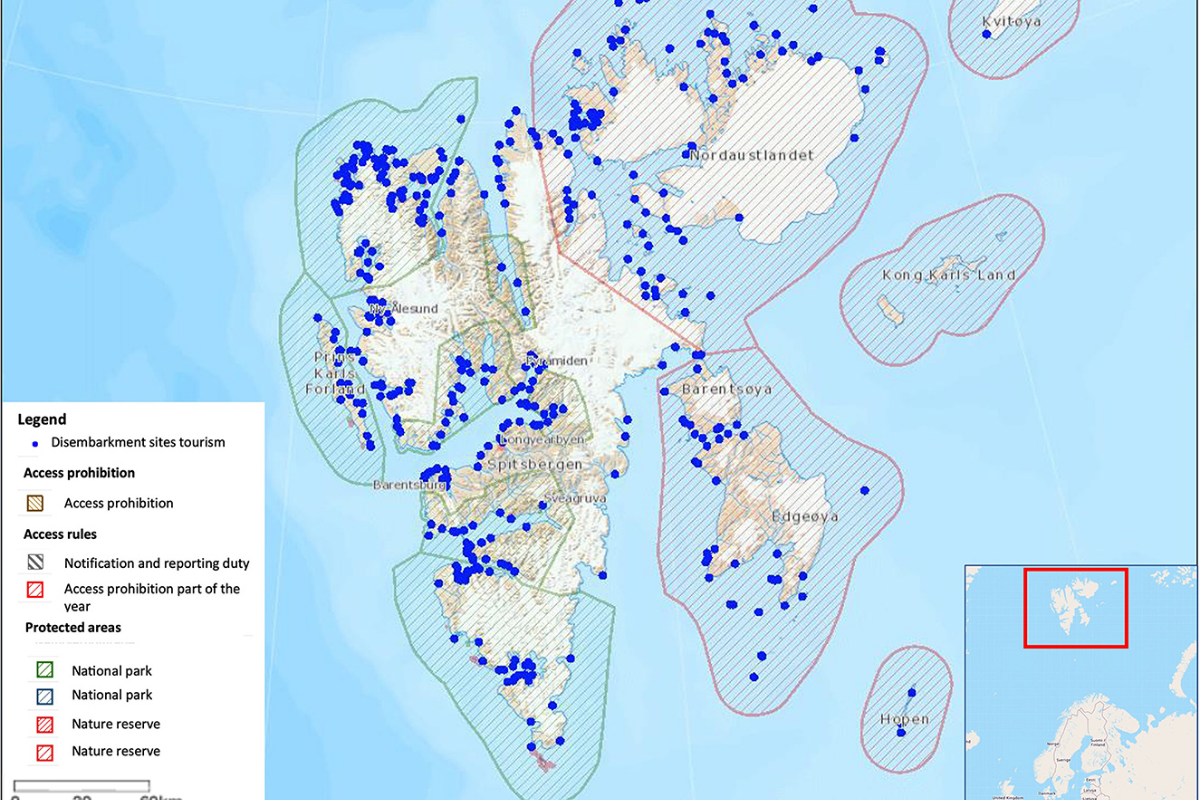
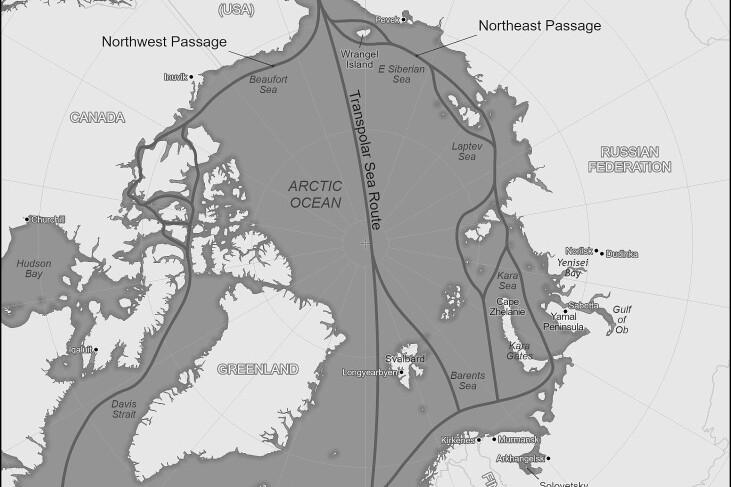
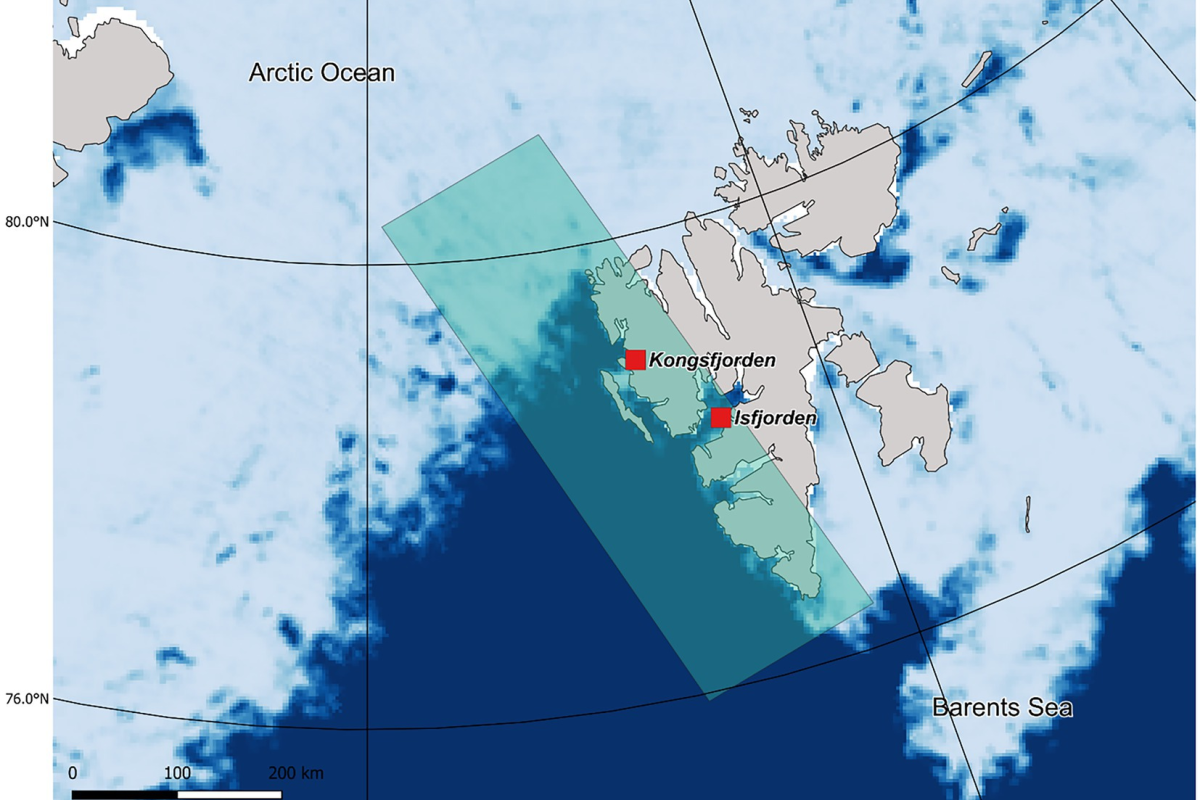
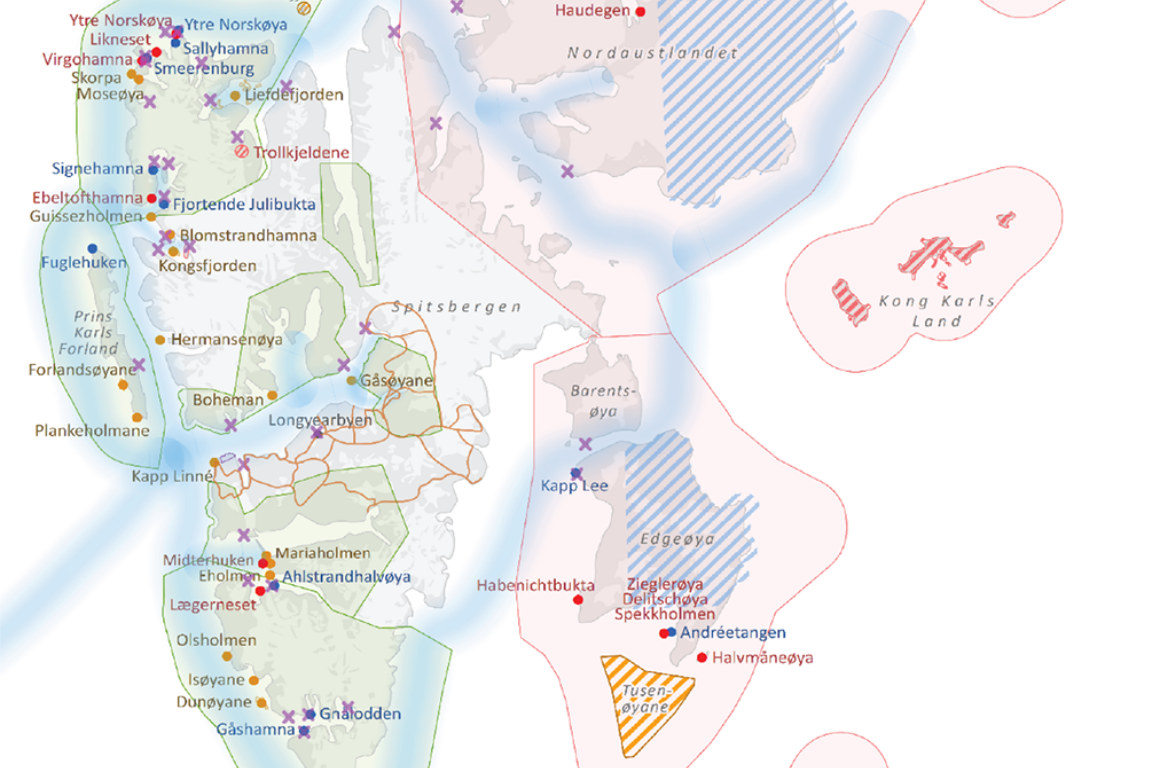
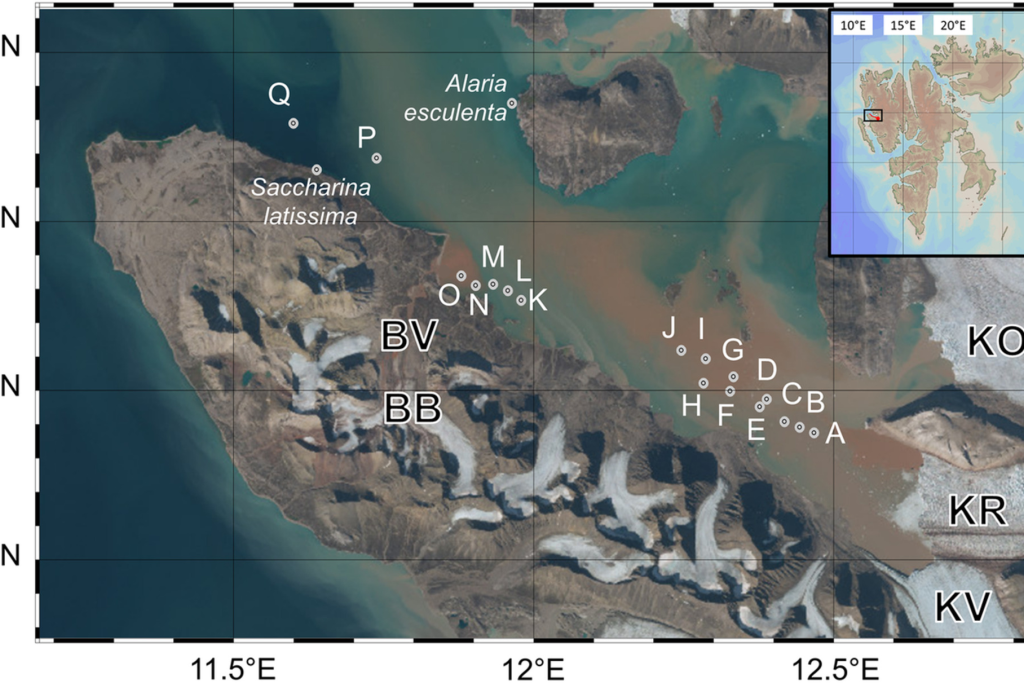
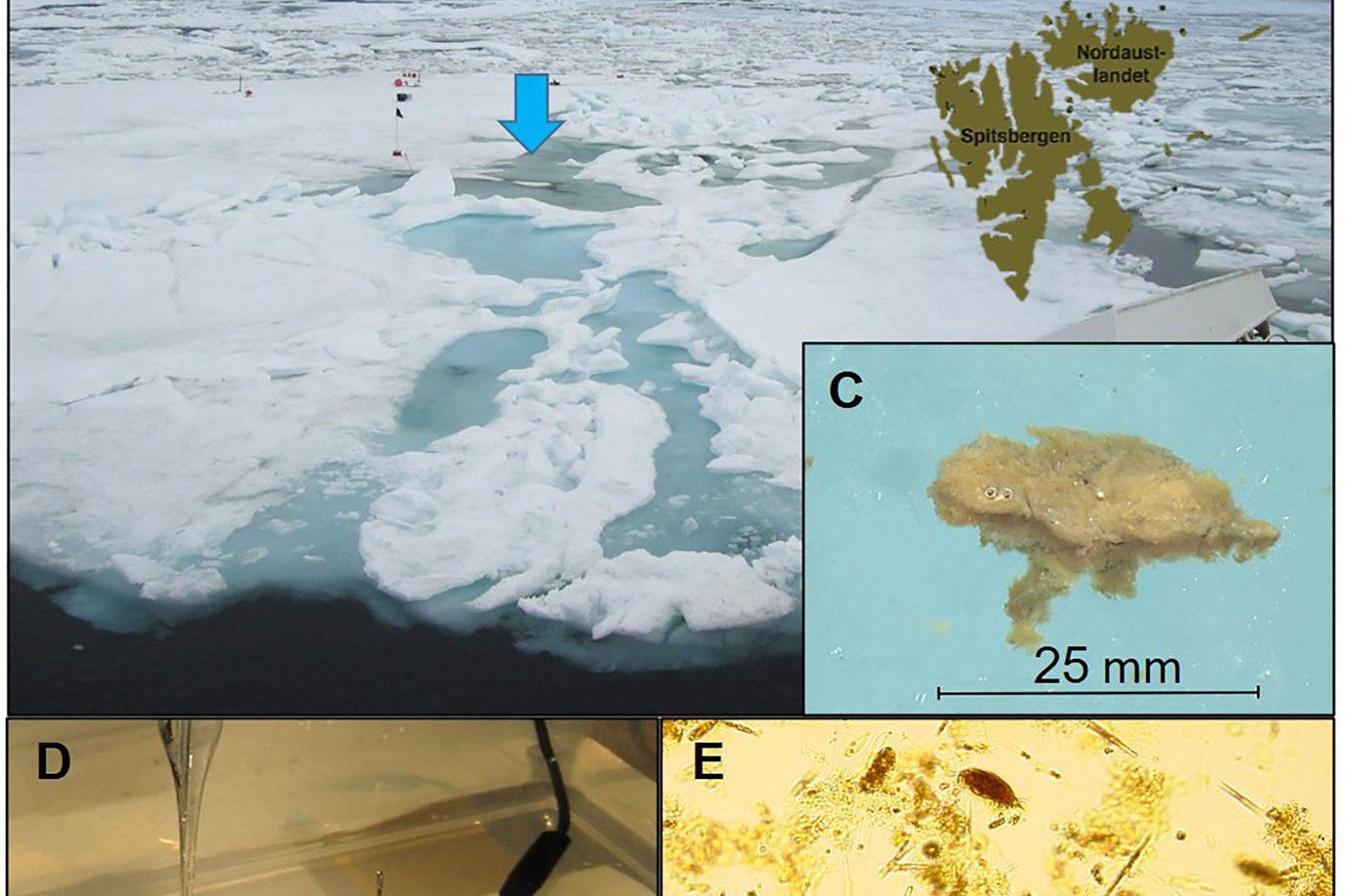
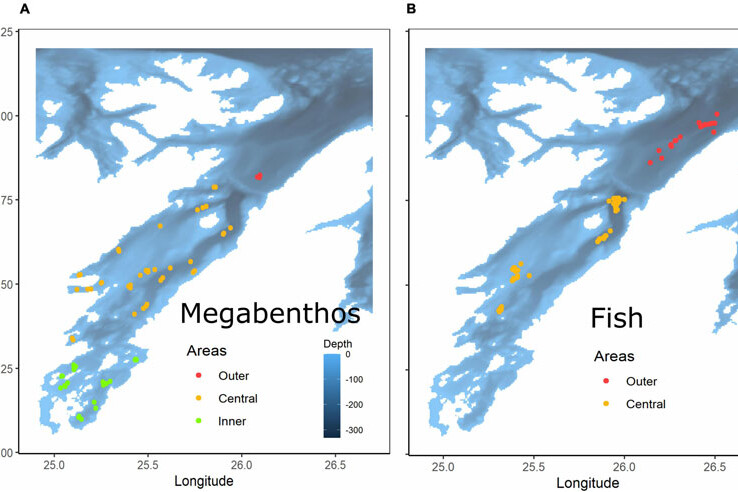
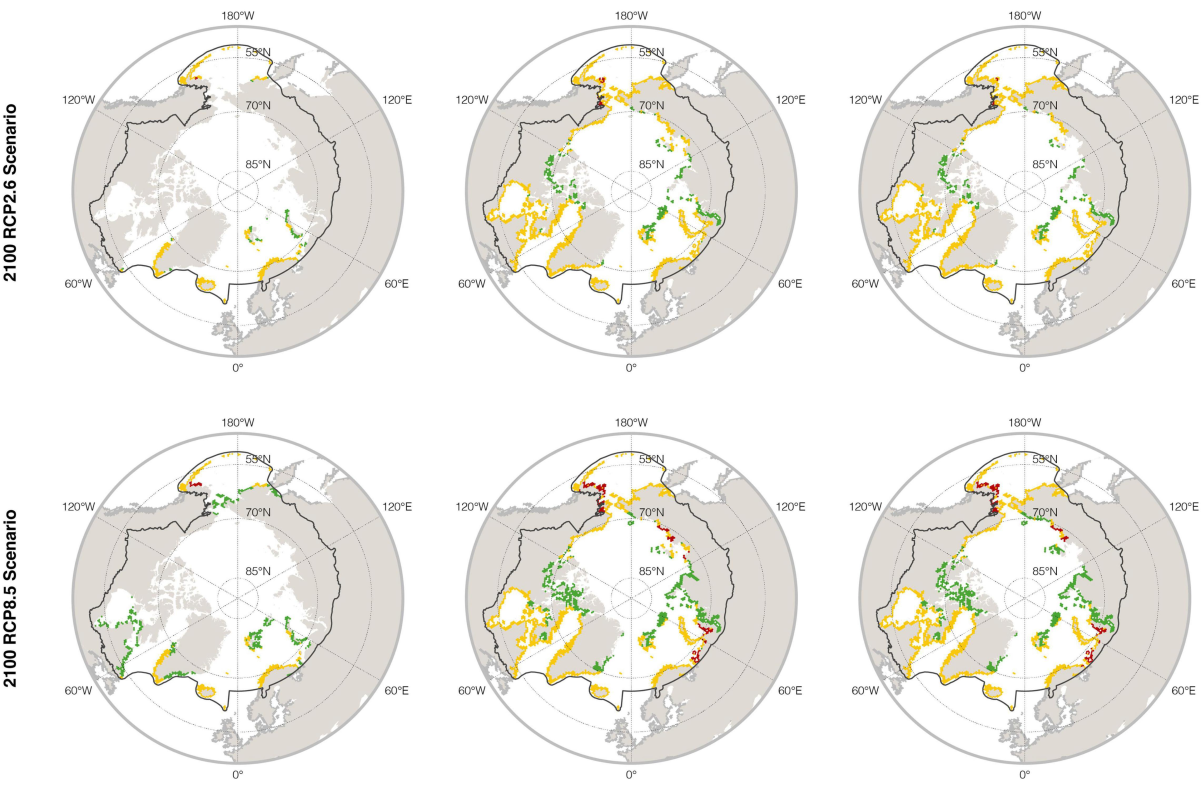
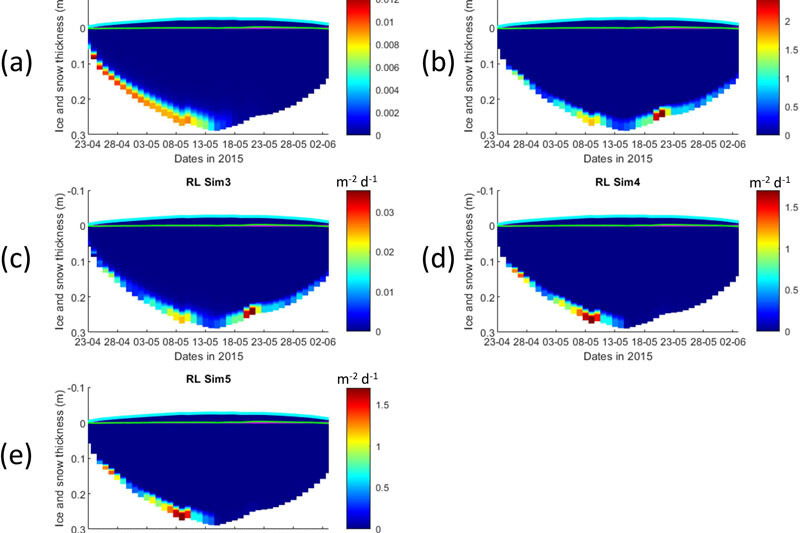
FACE IT
Here, you can find FACE-IT related news posts
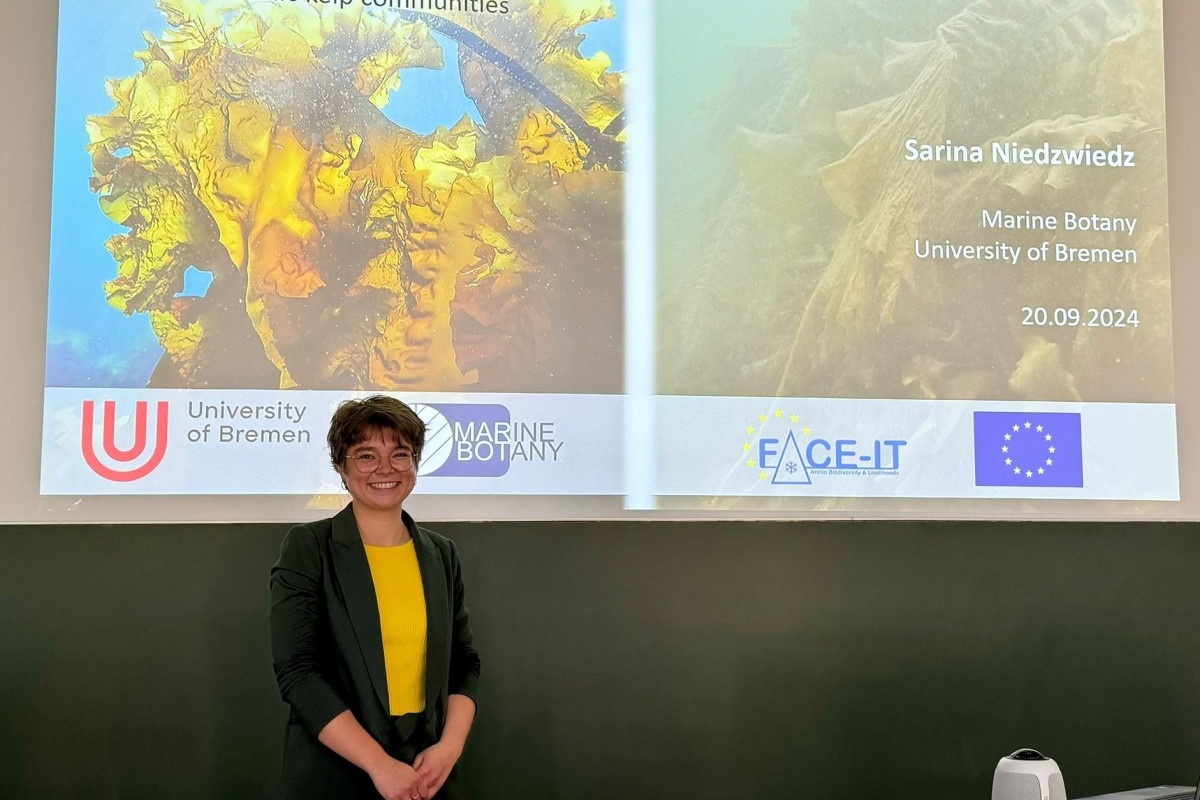
September 20, 2024
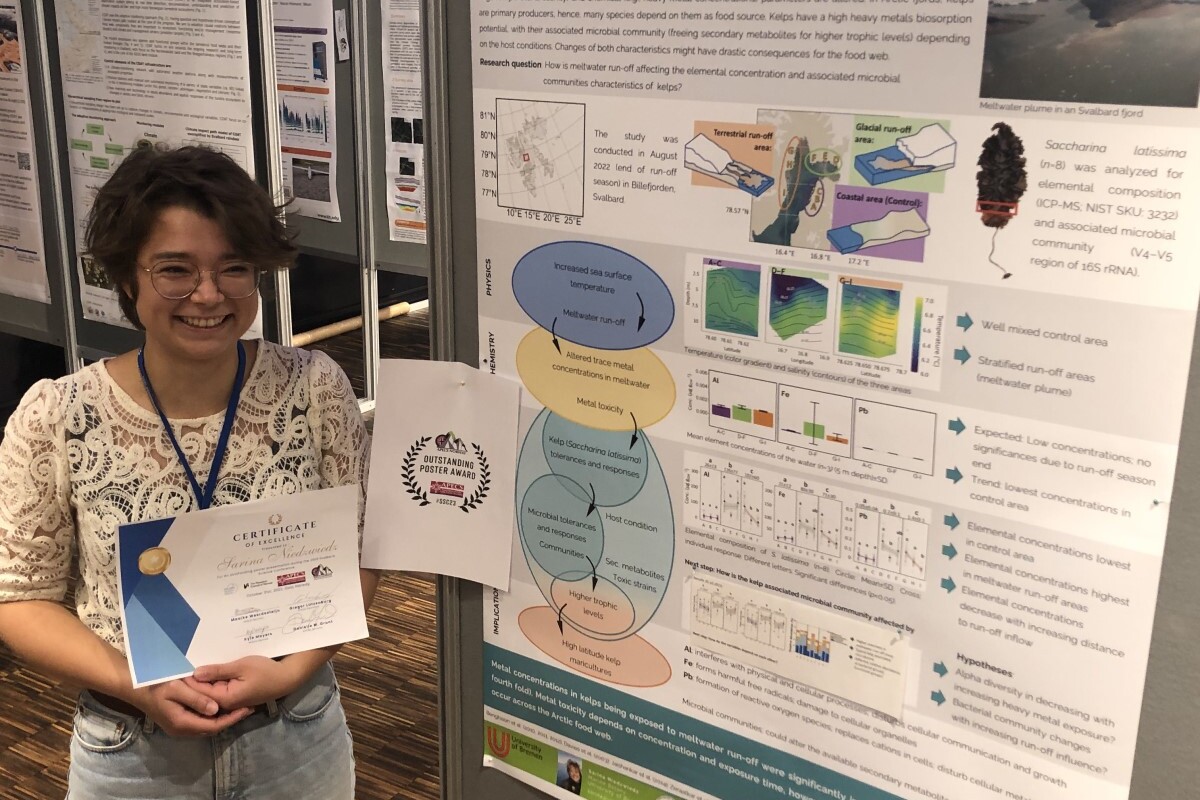
Sarina Niedzwiedz: Second PhD thesis defended within FACE-IT
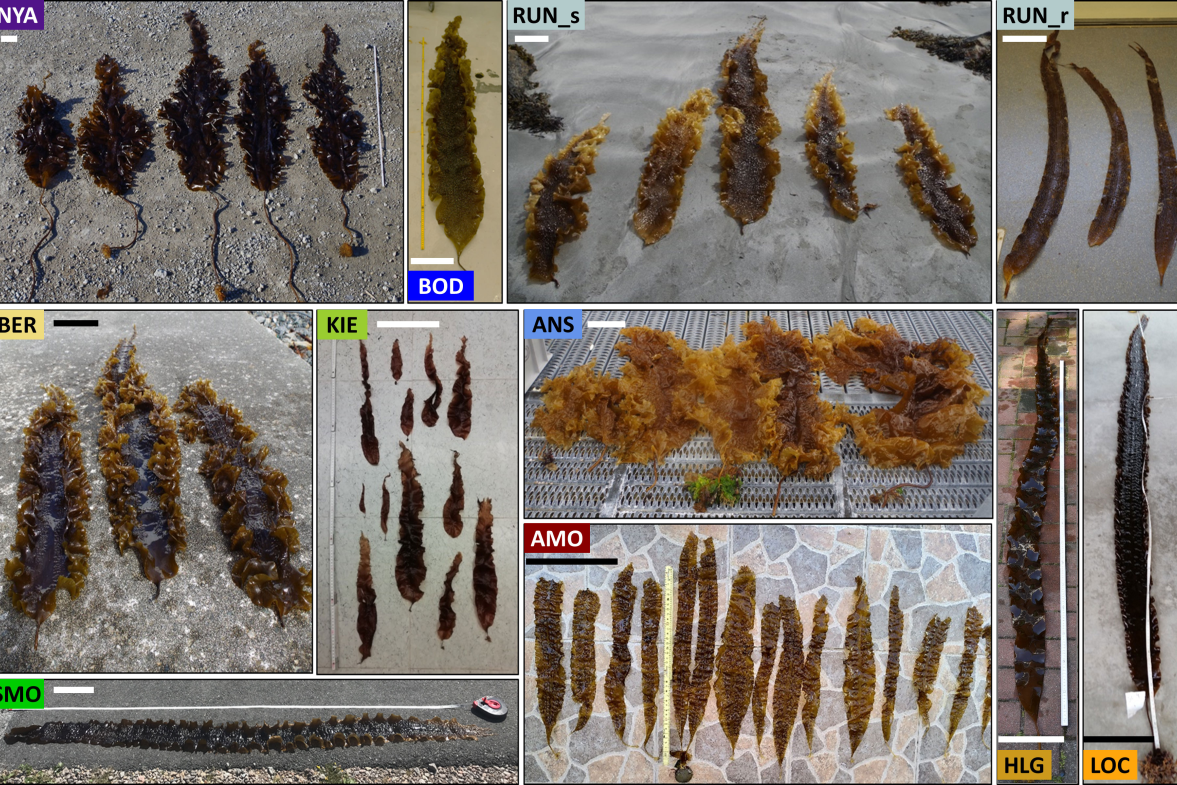
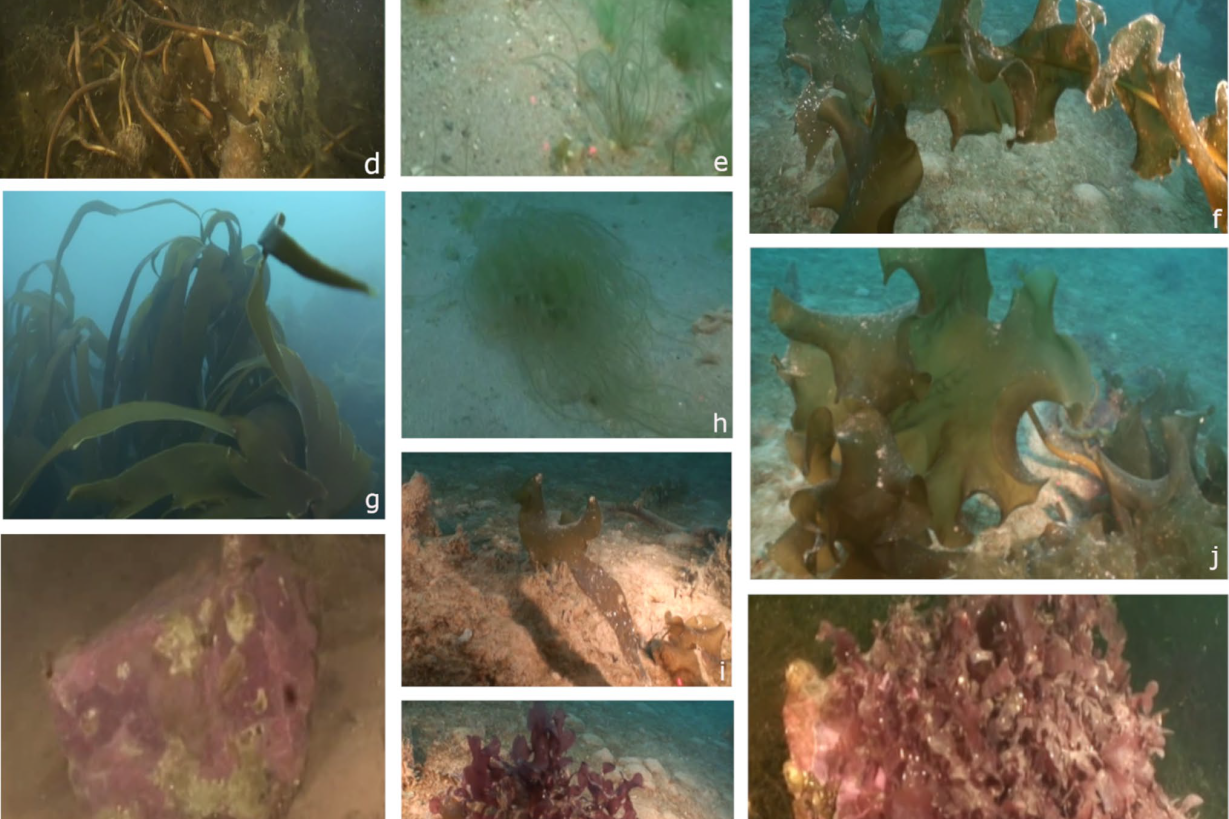
On 20 September 2024, Sarina Niedzwiedz successfully defended her PhD thesis, entitled "The Dark Side of Polar Day - The influence of coastal run-off on Arctic kelp communities". Sarina is working within the FACE-IT project at the department of Marine Botany at the University of Bremen, Germany.
September 2, 2024
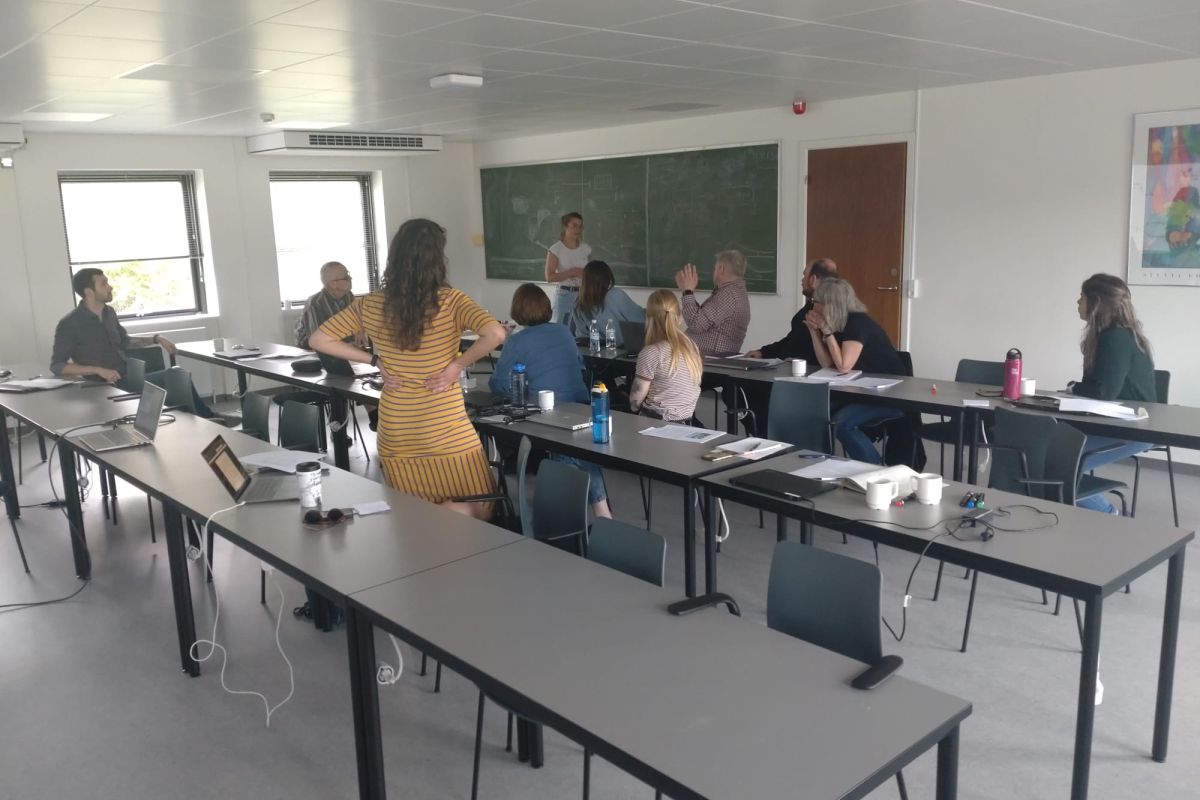
Last Annual Meeting of FACE-IT in Copenhagen, Denmark
FACE-IT is slowly coming towards its end. Yet, the whole team is still working on many different publications and many related activities. On 02 September 2024, the FACE-IT team held its official last annual meeting and general assembley at the campus of Aalborg University in Copenhagen, Denmark.
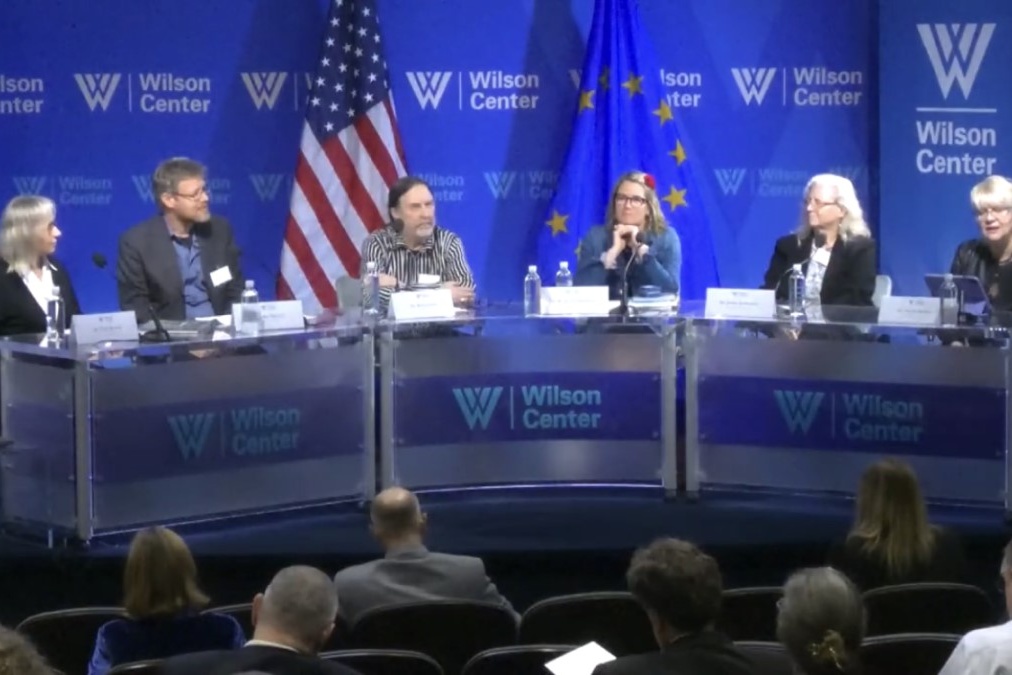
May 6, 2024
FACE-IT invited to expert panel on EU-US Arctic Cooperation
On 06 May, FACE-IT project coordinator Kai Bischof (Marine Botany, University of Bremen) participated as ecpert in a panel on EU-US Arctic cooperation, hosted by the Polar Institute and the Global Europe Program of the Wilson Center (Washington DC, US) and co-organized by the European Union.
October 25, 2023
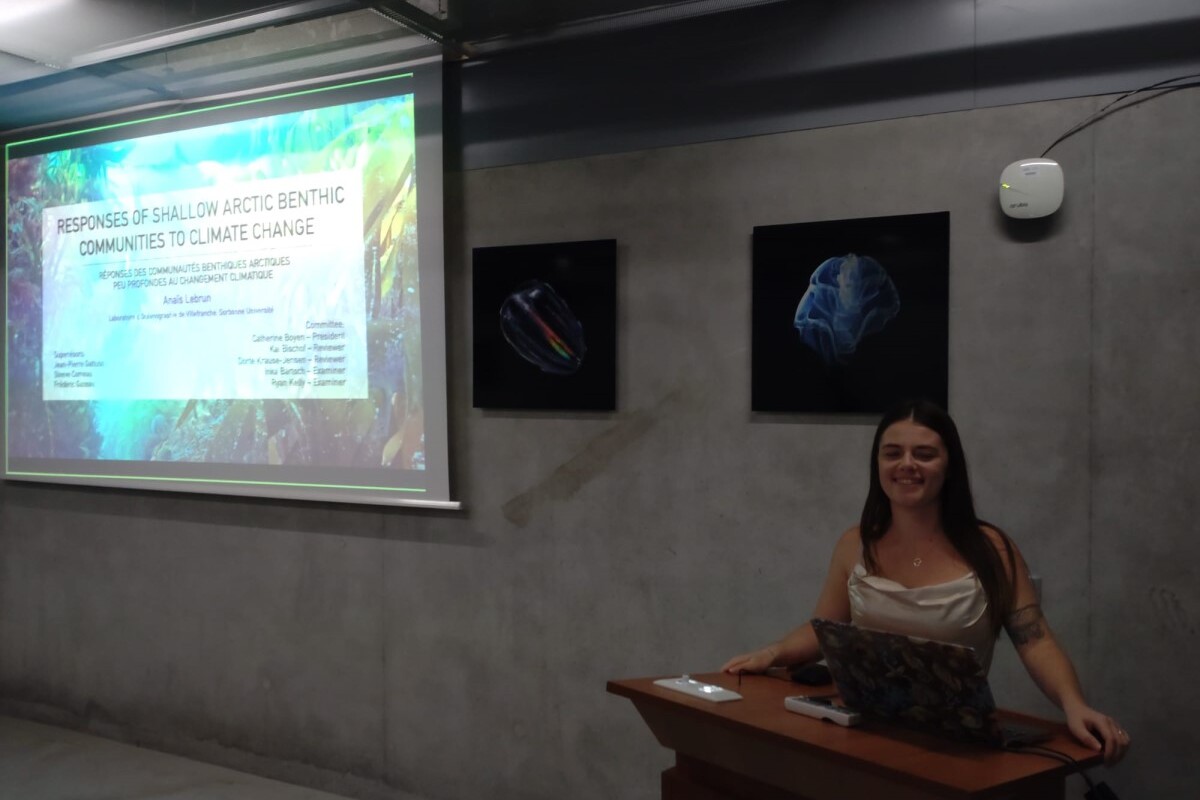
Anaïs Lebrun: First FACE-IT PhD thesis defended
On 23 October 2023, Anaïs Lebrun sucessfully defended her PhD thesis, entitled "Responses of shallow arctic benthic communities to climate change". Anaïs is working within the FACE-IT project at the Laboratoire d'Océanographie de Villefranche, LOV, which belongs to Sorbonne University.
May 17, 2023
FACE-IT Scientists Meet for Workshop on Ecosystem Function Changes in Rønbjerg, Denmark
From 14 to 17 May 2023, FACE-IT scientists involved in the research area Ecosystem Function Changes met at the field station of Aarhus University located at the Limfjord in Rønbjerg, Denmark.
April 24, 2023
Lill Rastad Bjørst from Denmark’s Aalborg University to Participate in Fulbright Arctic Week Activities in Washington D.C.
Dr. Lill Rastad Bjørst from Aalborg University is one of nineteen scholars who will take part in a series of events held in Washington, D.C. from April 24-28, 2023 as part of the Fulbright Arctic Initiative. Scholars from the Arctic Council’s eight member states will present their research and policy recommendations, capping two years of research and collaboration.
March 22, 2023
Master thesis project at the Greenland Institute of Natural Resources GINR, Nuuk
Phytoplankton primary production is the base of the marine food web. Consequently, productive areas are often important for benthic ecosystems, as well as fishery. Northern Melville Bay, in Northwest Greenland is north of the currently exploited fishing grounds, but important for vulnerable benthic organisms, including corals, sea pens, and sponges.
March 21, 2023
Successful Policy Briefing “Arctic Biodiversity, climate and food security” in Brussels
CHARTER, ECOTIP and FACE-IT, three EU-funded projects that are researching on biodiversity in relation to ice loss in the Arctic, organized jointly with the EU Polar Cluster a policy briefing in Brussels on 15 March 2023.
March 5, 2023
Two Master theses on plankton available at UNIS, Svalbard
The University Centre in Svalbard UNIS is running the northernmost high-frequent time series of plankton in the world studying the seasonal community development and biodiversity in Adventfjorden on the west coast of Svalbard. Since 2018, UNIS has expanded this timeseries to also cover the entire Svalbard archipelago by regularly sampling fjords in western, northern, eastern and southern Svalbard during summers using cruise ships as platform.
February 1, 2023
Policy Briefing “Arctic Biodiversity, climate and food security”
FACE-IT, ECOTIP and CHARTER, the three Horizon 2020 projects working on Arctic biodiversity and ice loss are conducting a policy briefing on 15 March 2023, 2 pm, in Brussels.
May 19, 2022
New Research Topic in “Frontiers in Marine Science”: Tourism and Outdoor Recreation in a Melting World
Halvor Dannevig from the Western Norway Research Institute is co-editing a new Research Topic in "Frontiers in Marine Science".
November 27, 2020
FACE-IT Kick-off Meeting
Four days full of information and getting to know new colleagues! The FACE-IT kick-off meeting took place from 23 to 26 November 2020.
November 26, 2020
„The new Arctic“ – public lectures to start FACE-IT
Right at the start of the FACE-IT project, the wide public was invited to attend a colloquium: “The new Arctic: Ecological and societal transitions in glacial fjord systems”. On 25 November, from 3:15 pm CET, experts from Greenland,
November 2, 2020
Official Start of FACE-IT
With November 1, 2020, we started the EU project FACE-IT (“The Future of Arctic coastal ecosystems – Identifying transitions in fjord systems and adjacent coastal areas”). FACE-IT is coordinated by Prof. Dr. Kai Bischof and Dr. Simon Jungblut from the University of Bremen. Marine Botany Group at the Department of Biology/Chemistry of the University of Bremen and compares Arctic fjord systems at different stages of glacial and sea-ice retreat in Greenland, Svalbard and the Norwegian Finmark.
SCIENTIFIC PUBLICATIONS
Photo © xyz
The scientists of FACE-IT are working inter and transdisciplinary across a wide spectrum of scientific fields. As peer-reviewed publications are the most important direct output of research, we aim to publish as much as possible in the open access mode. Below you can browse through all publications with FACE-IT contributions, with the newest ones on top.
September 29, 2024
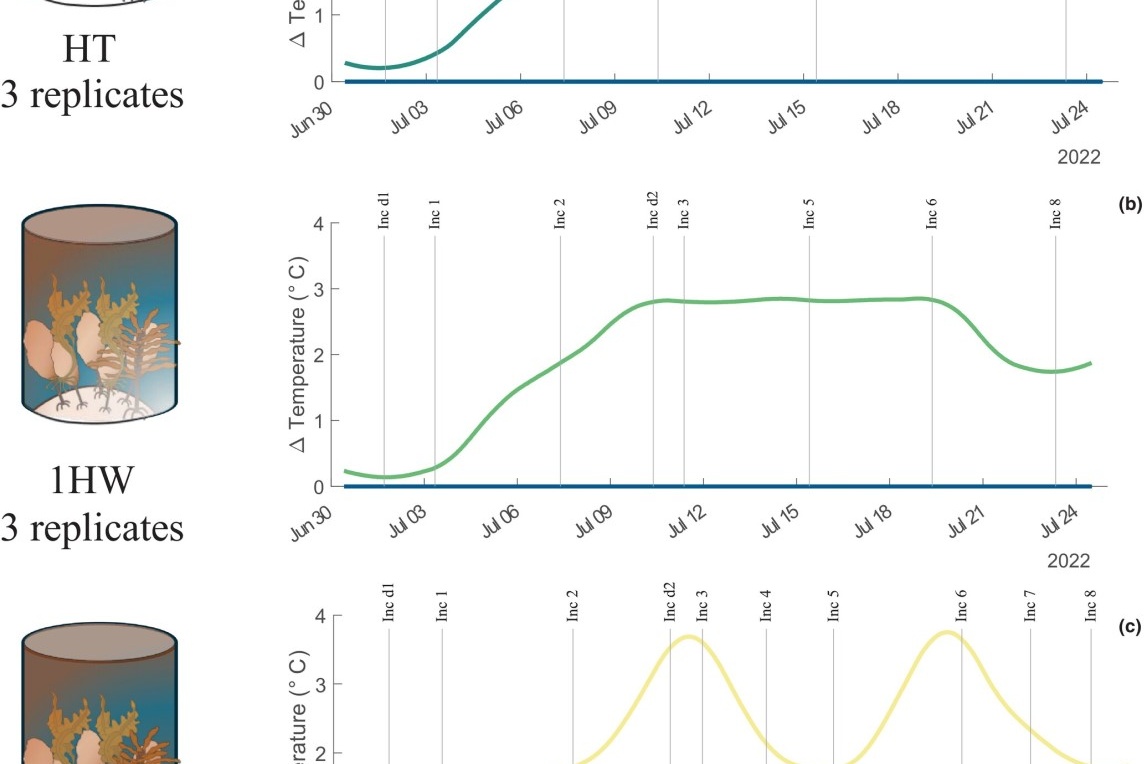
Summer primary production of Arctic kelp communities is more affected by duration than magnitude of simulated marine heatwaves
Fjord systems in the Norwegian Arctic are experiencing an increasing frequency and magnitude of marine heatwaves. These episodic heat stress events can have varying degrees of acute impacts on primary production and nutrient uptake of mixed kelp communities, as well as modifying the biogeochemical cycling in nearshore systems where vast areas of kelp create structural habitat.
September 12, 2024
Photoperiod and temperature interactions drive the latitudinal distribution of Laminaria hyperborea (Laminariales, Phaeophyceae) under climate change
Due to global rises in temperature, recent studies predict marine species shifting toward higher latitudes. We investigated the impact of interacting abiotic drivers on the distribution potential of the temperate kelp Laminaria hyperborea. The ecosystem engineering species is widespread along European coasts but has not yet been observed in the High Arctic, although it can survive several months of low temperatures and darkness.
September 10, 2024
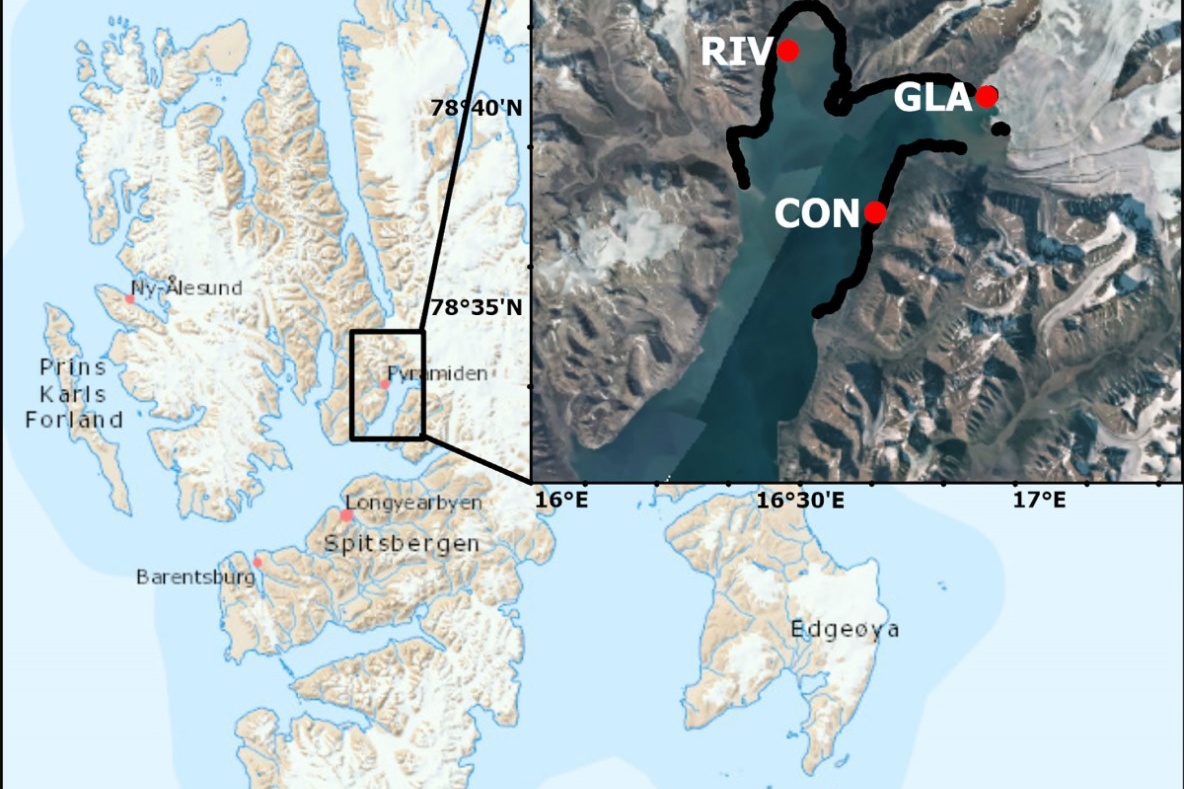
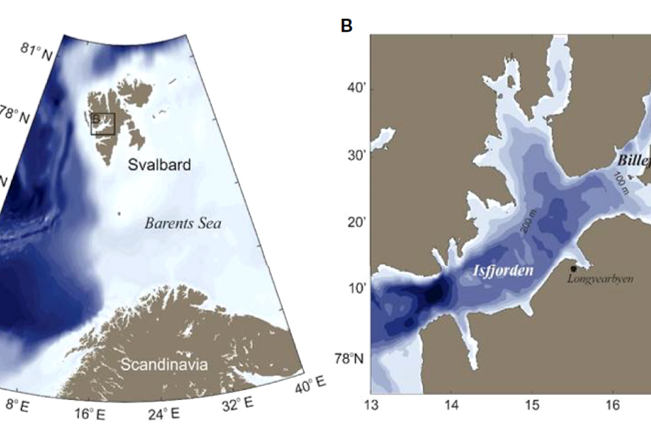
Acoustic mapping reveals macroalgal settlement following a retreating glacier front in the High Arctic
Vegetated coastal marine ecosystems are projected to expand northwards in the Arctic due to climate change, but the mechanisms for this expansion are complex and nuanced. Macroalgal biomass in the littoral areas of Svalbard has been increasing, but data at the glacier fronts are very scarce. In this study, we use hydroacoustics and video validation from an unmanned surface vehicle to survey macroalgal bed distribution along the coast of a High Arctic fjord (Billefjorden, Svalbard).
August 30, 2024
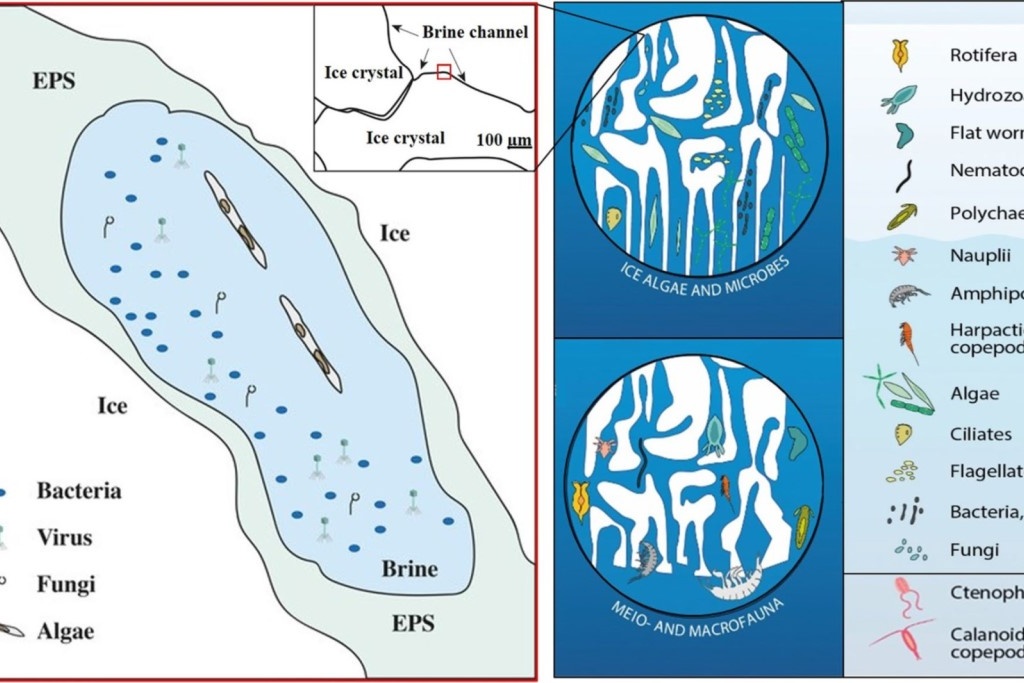
Sea ice as habitat for microalgae, bacteria, virus, fungi, meio- and macrofauna: A review of an extreme environment
The novel concept of the review is a focus on the organisms living in the sea ice and what mechanisms they have developed for their existence. The review describes the physical environment of the sea ice and the microorganisms living there as microalgae, bacteria, virus, fungi, meio- and macrofauna where they inhabit the brine channels and exposed to low temperatures as down to −25 °C and high salinities—up to 300.
July 28, 2024
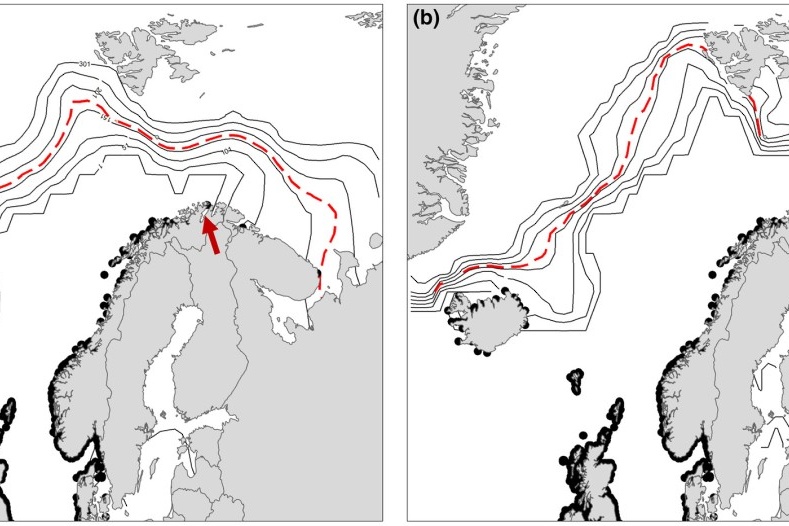
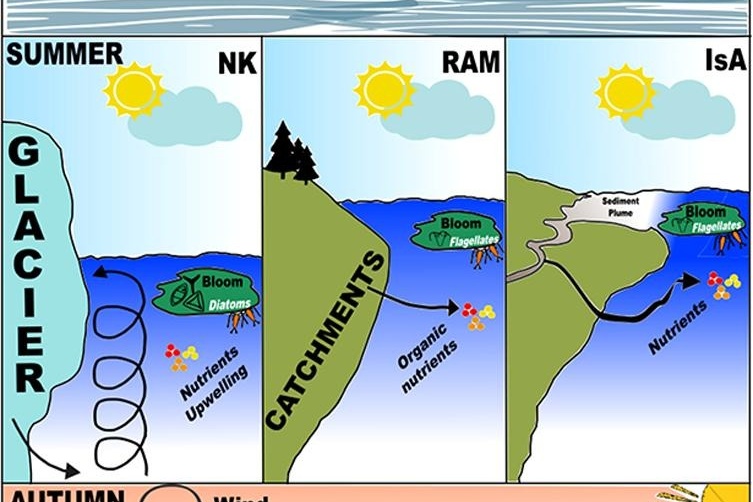
Seasonality in phytoplankton communities and production in three Arctic fjords across a climate gradient
Phytoplankton communities and production in Arctic fjords undergo strong seasonal variations. Phytoplankton blooms are periods with high primary production, leading to elevated algal biomass fueling higher trophic levels. Blooms are typically driven bottom-up by light and nutrient availability but may also be top-down controlled by grazing. While phytoplankton spring blooms are common across all Arctic systems, summer and autumn blooms and their drivers are less predictable.
July 23, 2024
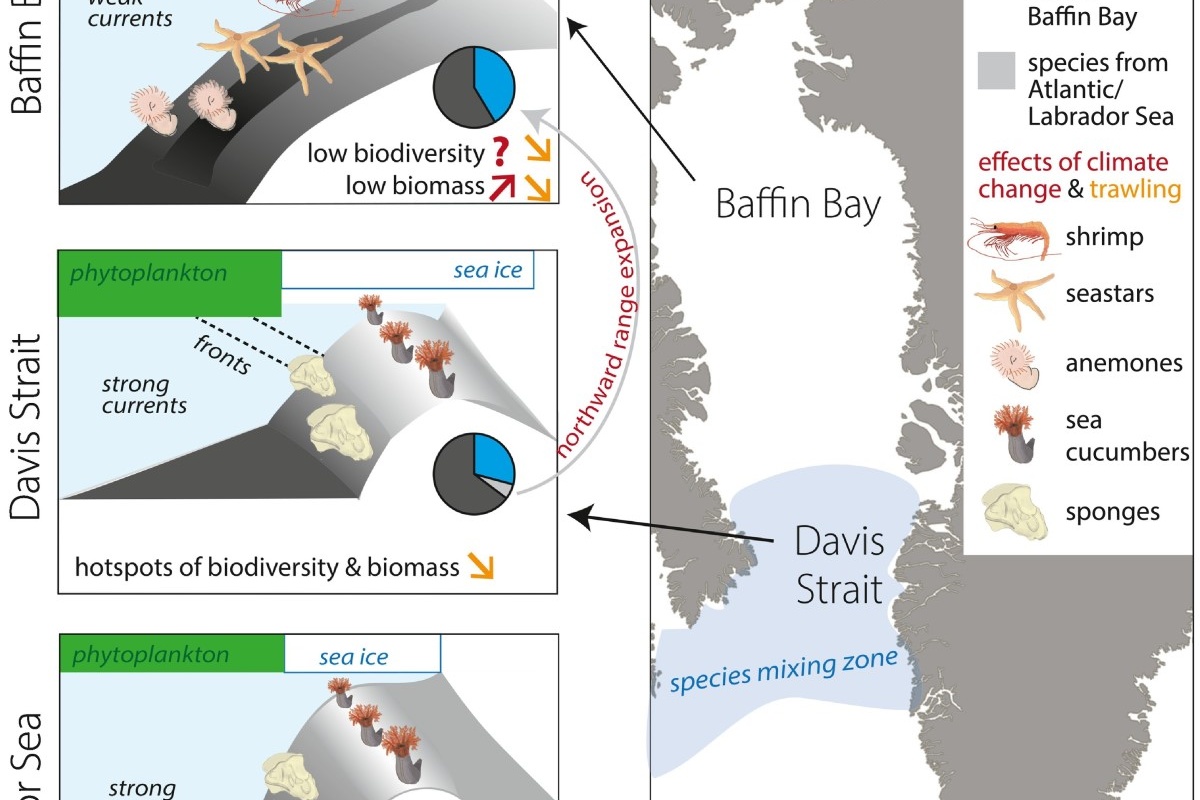
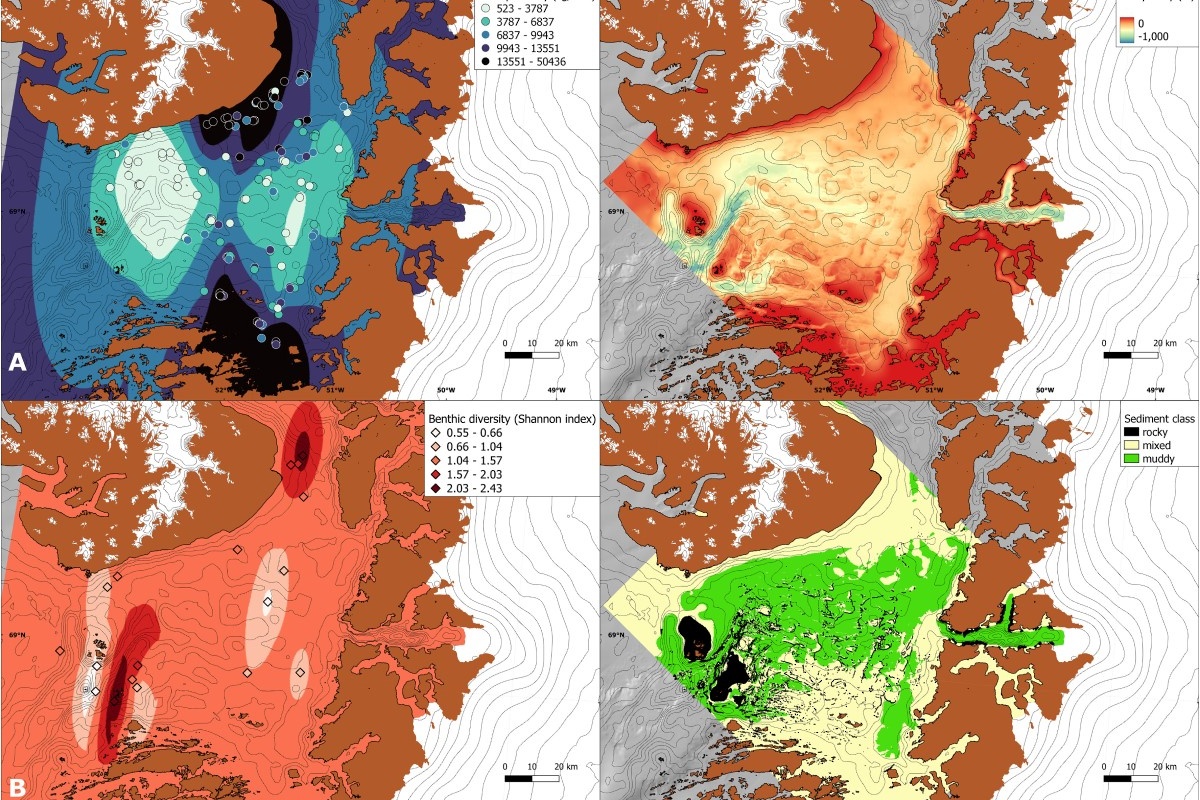
Arctic benthos in the Anthropocene: Distribution and drivers of epifauna in West Greenland
Albeit remote, Arctic benthic ecosystems are impacted by fisheries and climate change. Yet, anthropogenic impacts are poorly understood, as benthic ecosystems and their drivers have not been mapped over large areas. We disentangle spatial patterns and drivers of benthic epifauna (animals living on the seabed surface) in West Greenland, by integrating an extensive beam-trawl dataset (326 stations, 59–75°N, 30–1400 m water depth) with environmental data.
June 25, 2024
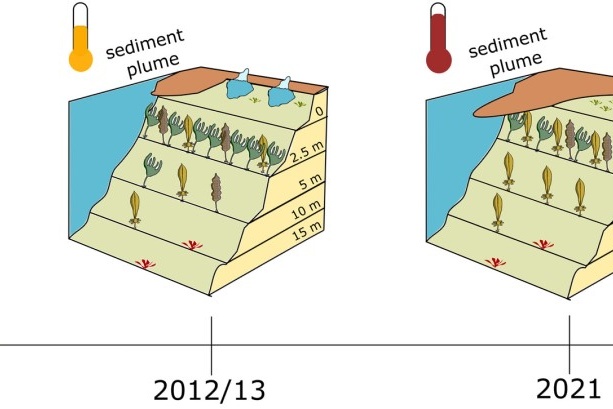
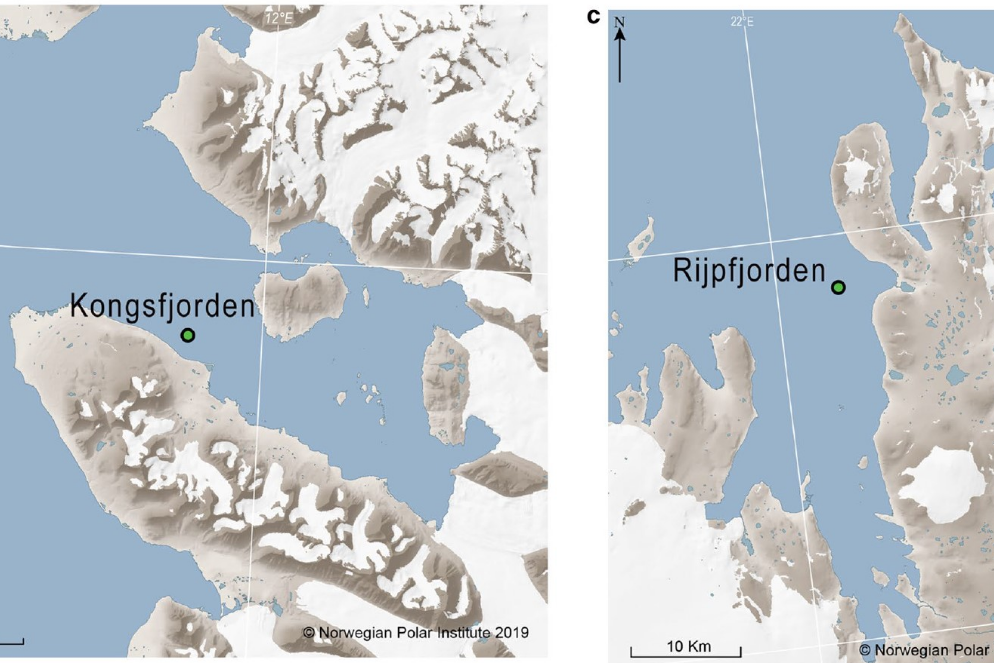
Kelp forest community structure and demography in Kongsfjorden (Svalbard) across 25 years of Arctic warming
The Arctic archipelago of Svalbard is a hotspot of global warming and many fjords experience a continuous increase in seawater temperature and glacial melt while sea-ice cover declines. In 1996/1998, 2012–2014, and 2021 macroalgal biomass and species diversity were quantified at the study site Hansneset, Kongsfjorden (W-Spitsbergen) in order to identify potential changes over time.
June 14, 2024
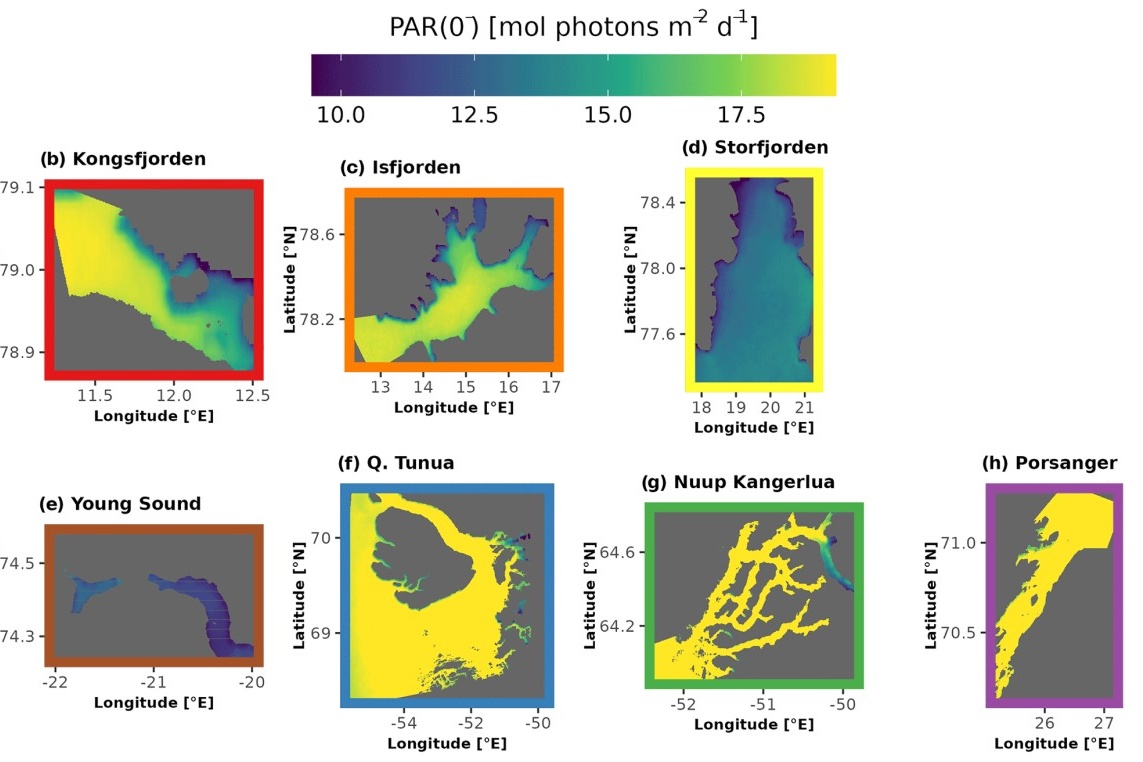
Underwater light environment in Arctic fjords
Most inhabitants of the Arctic live near the coastline, which includes fjord systems where socio-ecological coupling with coastal communities is dominant. It is therefore critically important that the key aspects of Arctic fjords be measured as well as possible. Much work has been done to monitor temperature and salinity, but in-depth knowledge of the light environment throughout Arctic fjords is lacking.
June 10, 2024
An Arctic sea ice spring bloom driven and dominated by Dinoflagellates – a harbinger of the future sea ice?
The sea ice spring bloom is crucial for sustaining Arctic marine food webs, with sea ice algae serving as primary carbon sources for higher trophic levels. Despite the prevailing dominance of diatom species in sea ice spring blooms, our study highlights a notable deviation, showcasing a bloom driven by dinoflagellates.
April 23, 2024
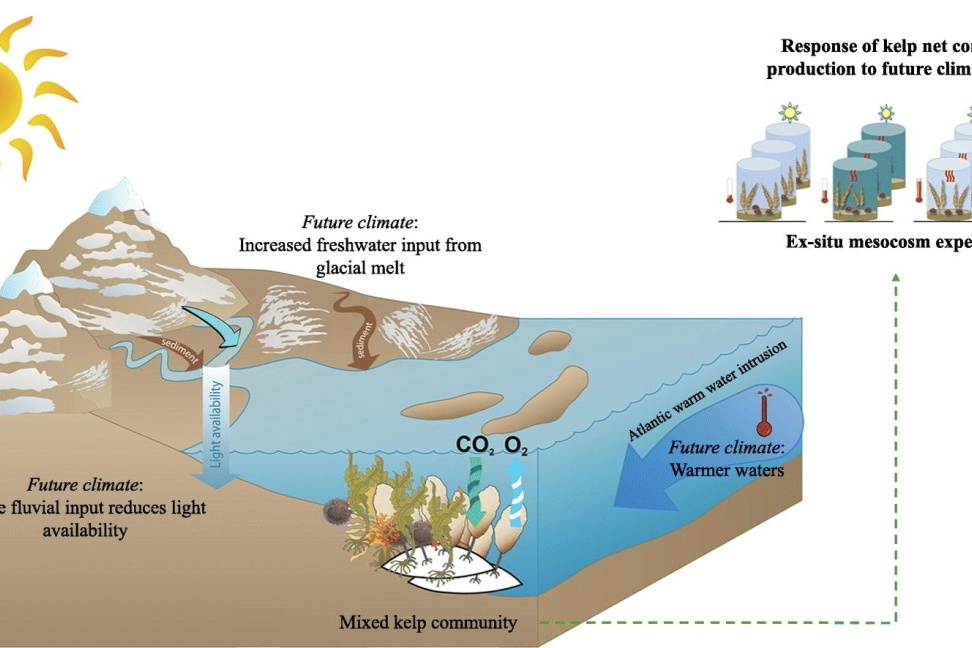
Productivity of mixed kelp communities in an Arctic fjord exhibit tolerance to a future climate
Arctic fjords are considered to be one of the ecosystems changing most rapidly in response to climate change. In the Svalbard archipelago, fjords are experiencing a shift in environmental conditions due to the Atlantification of Arctic waters and the retreat of sea-terminating glaciers. These environmental changes are predicted to facilitate expansion of large, brown macroalgae, into new ice-free regions.
April 23, 2024
Arctic puzzle: Pioneering a northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) habitat model in Disko Bay, West Greenland
Recent advancements in spatial modelling leverage remote sensing data and statistical species-environment relationships to forecast the distribution of a specific species. Our study focuses on Disko Bay in West Greenland, recognized as a significant marine biodiversity hotspot in the region.
April 9, 2024
EU Engagement in the Arctic: Challenges to Achieving Ambitions in an Area outside Its Jurisdiction
The European Union (EU) has underscored its will to heighten its engagement in the Arctic region. Beyond traditional areas of interest – such as tackling climate change, supporting research and developing cooperations – critical resources and security emerged as new topics in the EU’s most recent policy documents.
March 20, 2024
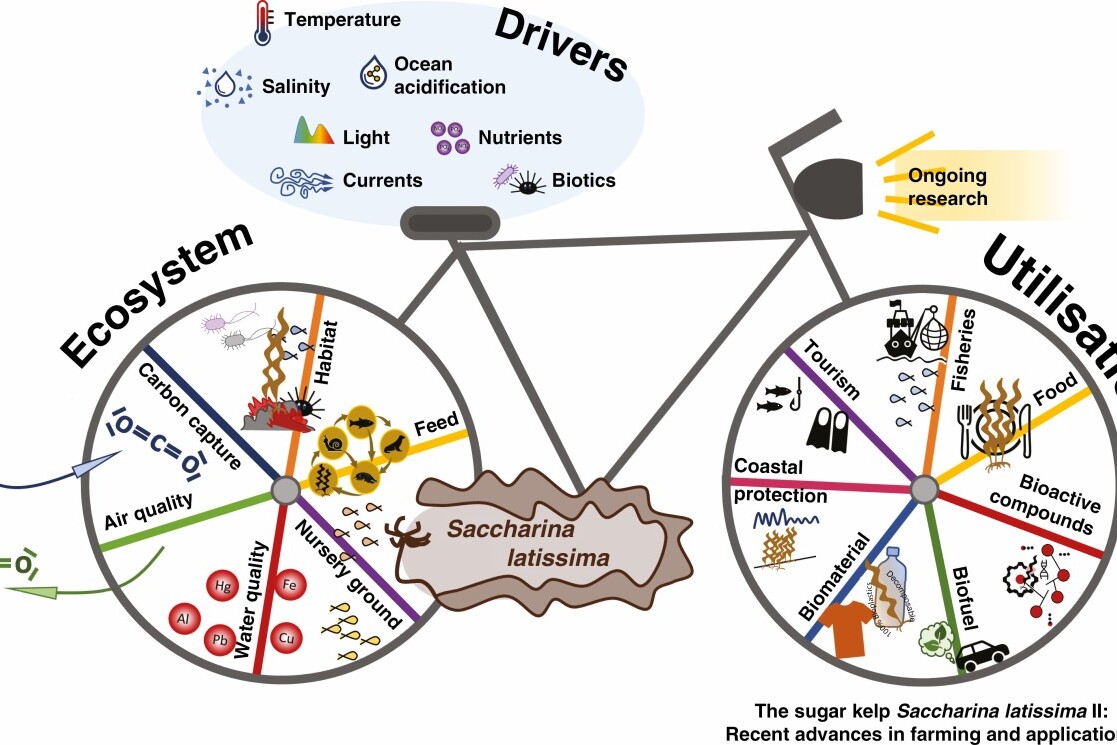
The sugar kelp Saccharina latissima II: Recent advances in farming and applications
The sugar kelp Saccharina latissima has received intense scientific attention over the last decades. In recent years, interest in cultivation of the species has strongly increased in the North Atlantic Ocean and the Eastern Pacific Ocean, driven by the great potential of S. latissima to be utilised for various industrial applications, including food, feed, and biomaterials.
March 13, 2024
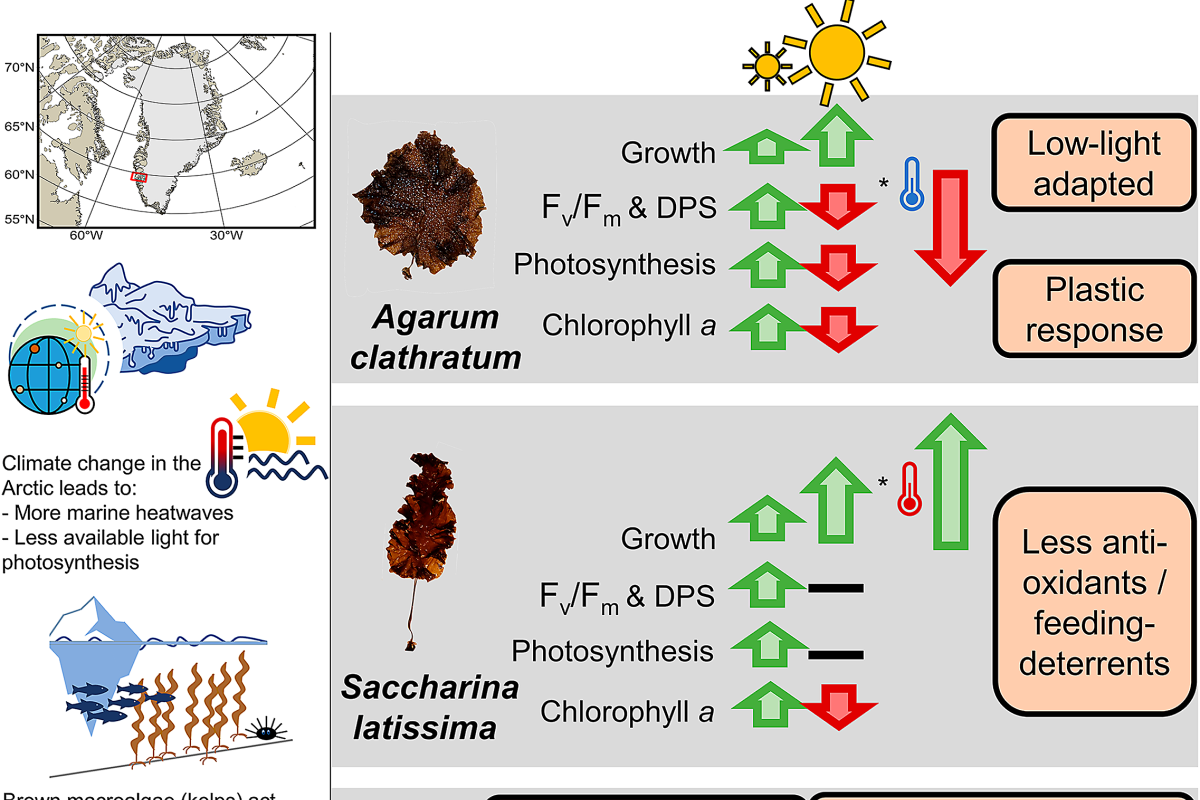
Light-mediated temperature susceptibility of kelp species (Agarum clathratum, Saccharina latissima) in an Arctic summer heatwave scenario
Kelps (Phaeophyceae, Laminariales) are ecosystem engineers along Arctic rocky shores. With ongoing climate change, the frequency and intensity of marine heatwaves are increasing. Further, extensive meltwater plumes darken Arctic fjords.
March 4, 2024
Seafloor primary production in a changing Arctic Ocean
Phytoplankton and sea ice algae are traditionally considered to be the main primary producers in the Arctic Ocean. In this Perspective, we explore the importance of benthic primary producers (BPPs) encompassing microalgae, macroalgae, and seagrasses, which represent a poorly quantified source of Arctic marine primary production. Despite scarce observations, models predict that BPPs are widespread, colonizing ~3 million km2 of the extensive Arctic coastal and shelf seas.
February 8, 2024
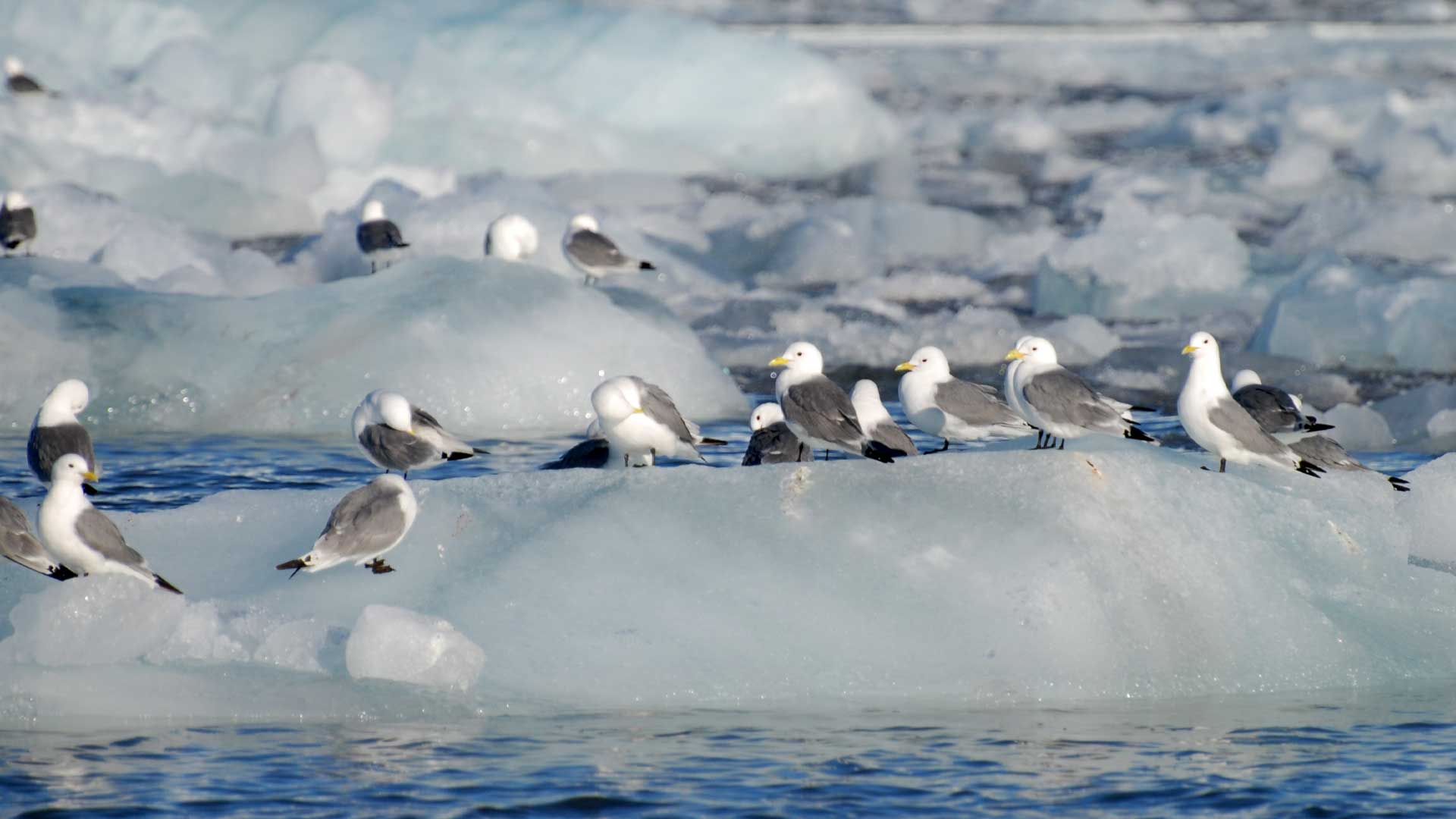
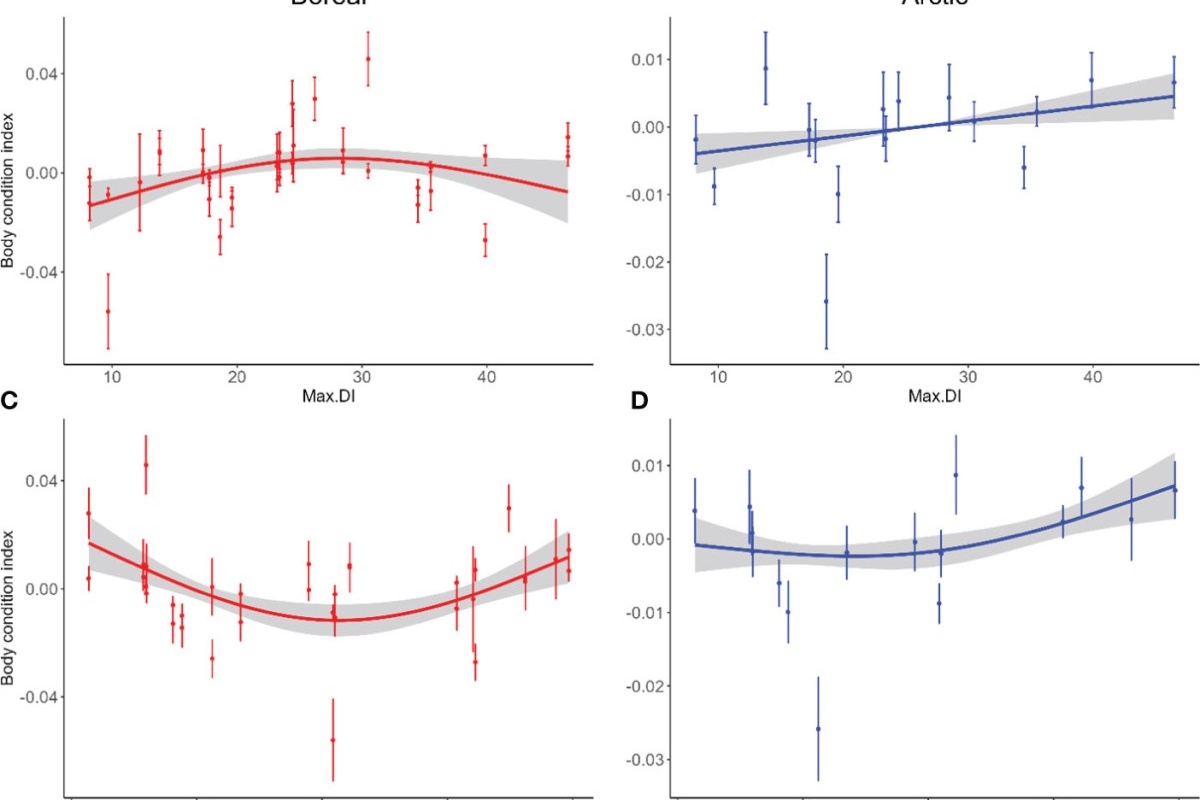
Ice type matters: impacts of landfast and drift ice on body condition in a high Arctic seabird community
Sea ice, a central component of polar ecosystems, is undergoing profound changes due to climate change. In particular, the Arctic is experiencing unprecedented warming at quicker rates than other regions. This alarming trend of sea ice loss has dire consequences, with spill-over effects on the entire ecosystem, from phytoplankton to top predators.
January 24, 2024
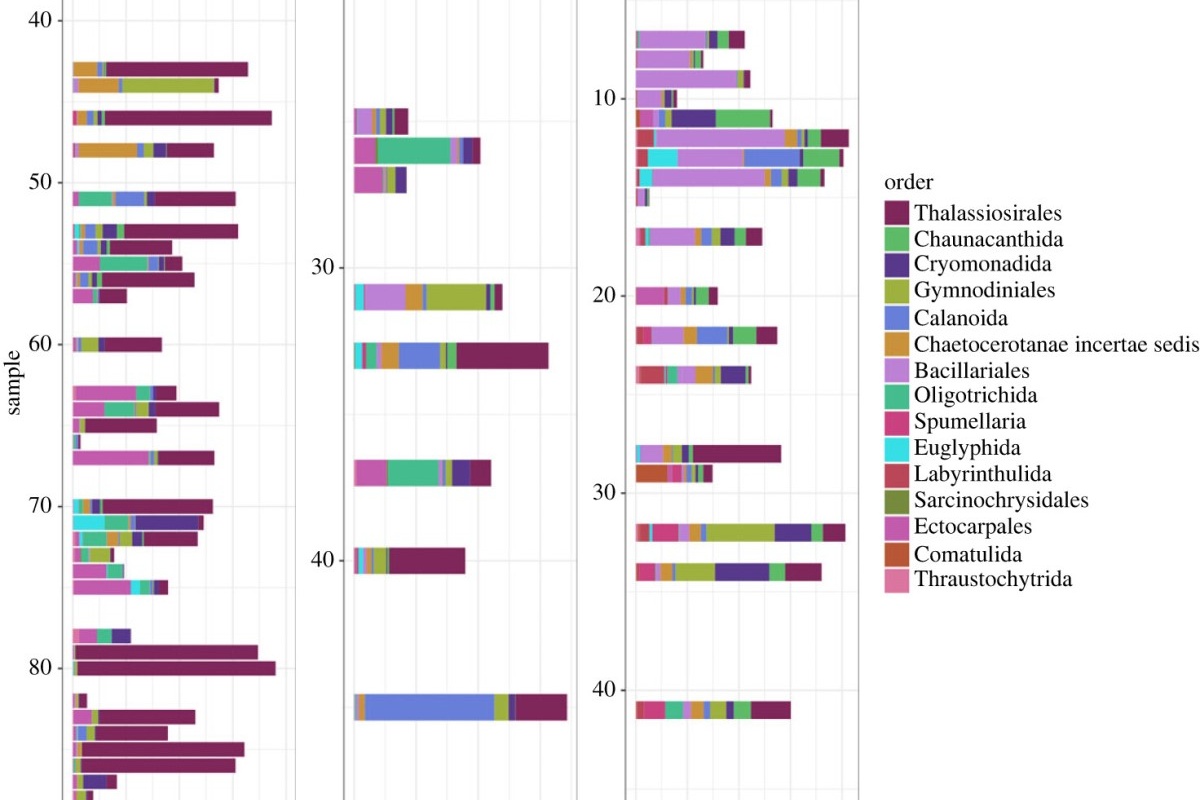
Environmental drivers of Arctic communities based on metabarcoding of marine sediment eDNA
Our ability to assess biodiversity at relevant spatial and temporal scales for informing management is of increasing importance given this is foundational to identify and mitigate the impacts of global change. Collecting baseline information and tracking ecological changes are particularly important for areas experiencing rapid changes and representing data gaps such as Arctic marine ecosystems.
January 17, 2024
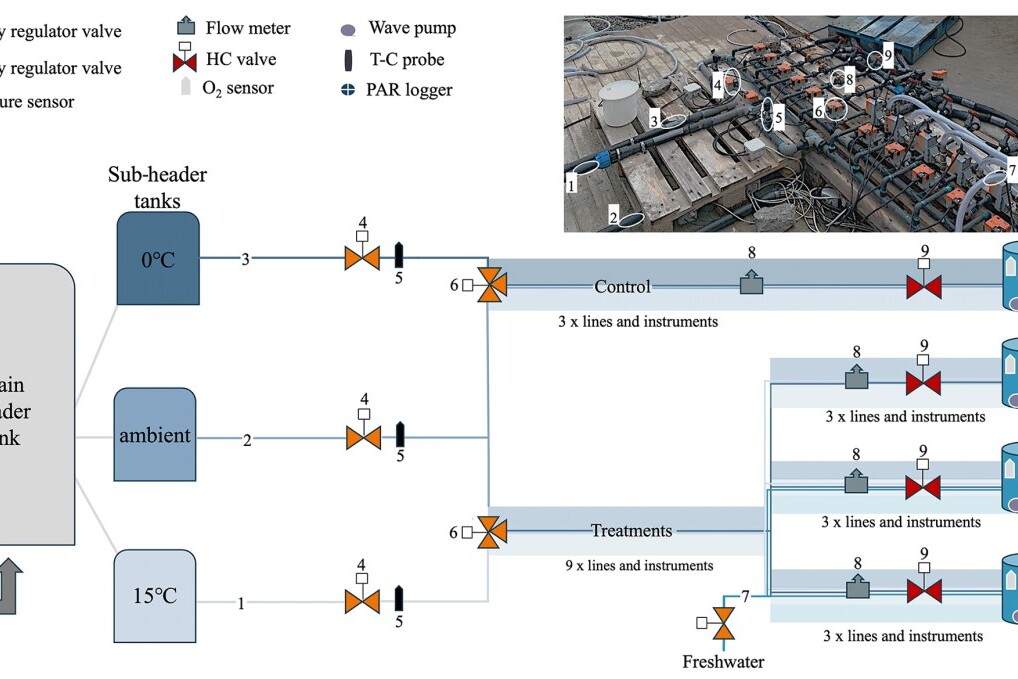
Technical note: An autonomous flow-through salinity and temperature perturbation mesocosm system for multi-stressor experiments
The rapid environmental changes in aquatic systems as a result of anthropogenic forcings are creating a multitude of challenging conditions for organisms and communities. The need to better understand the interaction of environmental stressors now, and in the future, is fundamental to determining the response of ecosystems to these perturbations.
December 18, 2023
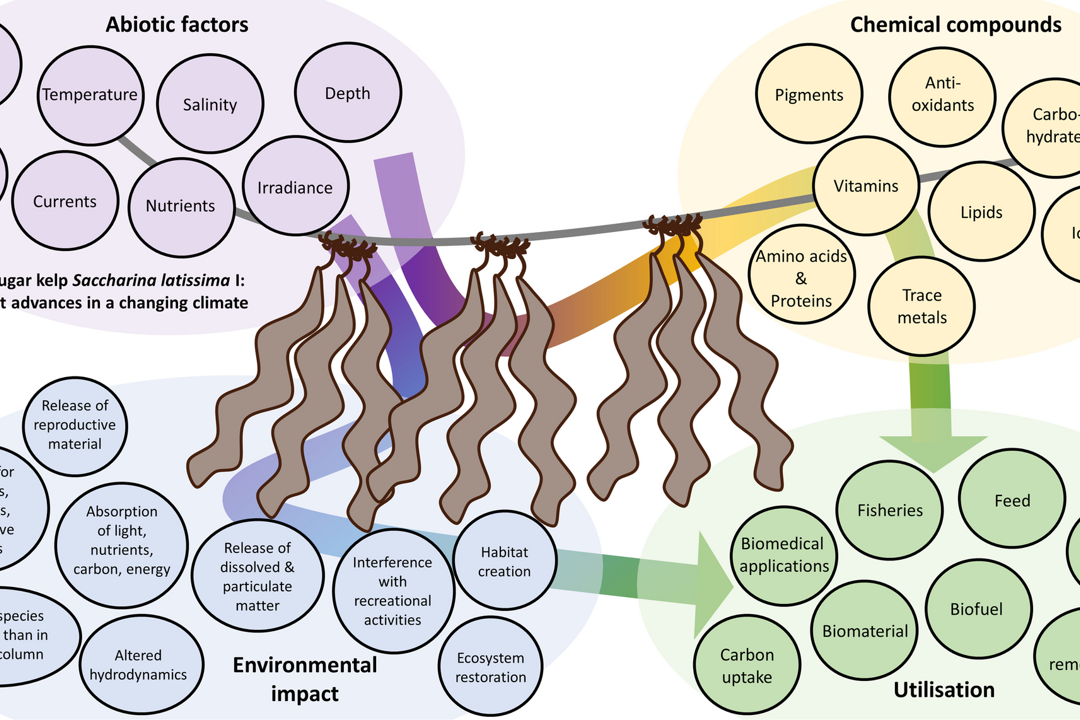
The sugar kelp Saccharina latissima I: recent advances in a changing climate
The sugar kelp Saccharina latissima is a Laminariales species widely distributed in the Northern Hemisphere. Its physiology and ecology have been studied since the 1960s, given its ecological relevance on western temperate coasts.
December 9, 2023
Arctic infrastructure: Considerations in the green transition
The global green transition has put a new focus on the Arctic region and its resources (eg.energy, minerals, and access to land) at the same time as Arctic communities are looking for development, self-determination, and growth.
December 9, 2023
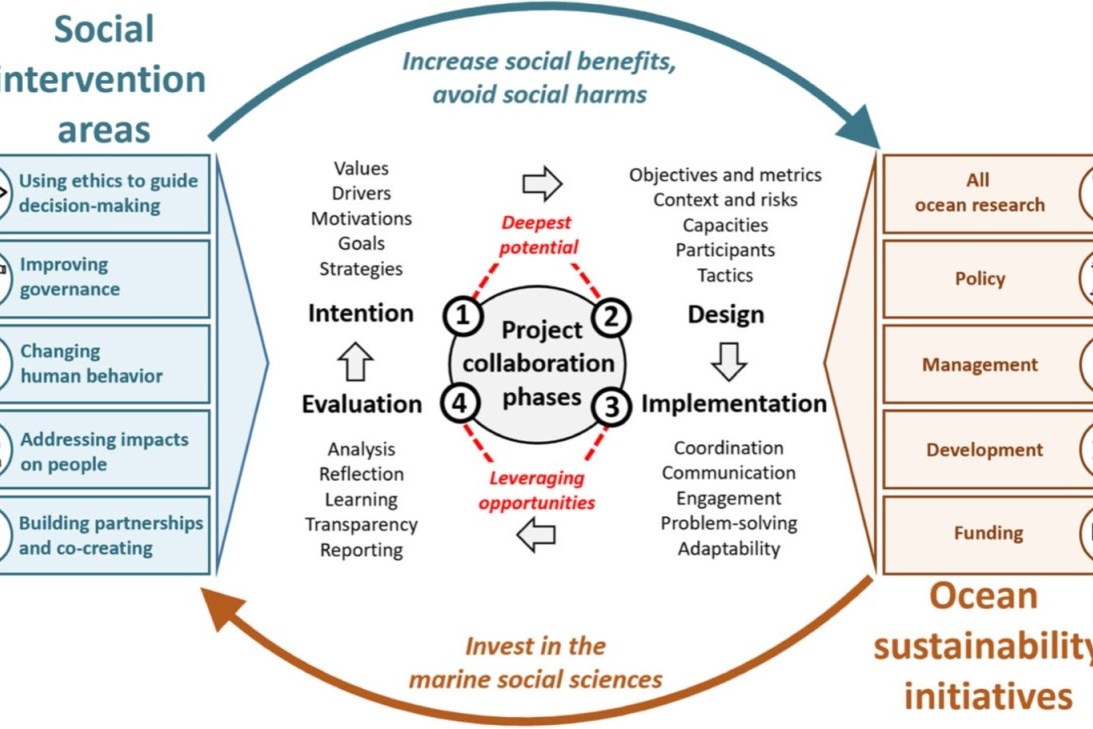
Five social science intervention areas for ocean sustainability initiatives
Ocean sustainability initiatives – in research, policy, management and development – will be more effective in delivering comprehensive benefits when they proactively engage with, invest in and use social knowledge. We synthesize five intervention areas for social engagement and collaboration with marine social scientists, and in doing so we appeal to all ocean science disciplines and non-academics working in ocean initiatives in industry, government, funding agencies and civil society.
October 28, 2023
Spatial Variability in the Primary Production Rates and Biomasses (Chl a) of Sea Ice Algae in the Canadian Arctic–Greenland Region: A Review
The aims of this review are to elucidate the spatial variation in the primary production rates and biomasses (Chl a) of sea ice algae in the Canadian Arctic–Greenland region, characterized by its comparable physical settings.
October 11, 2023
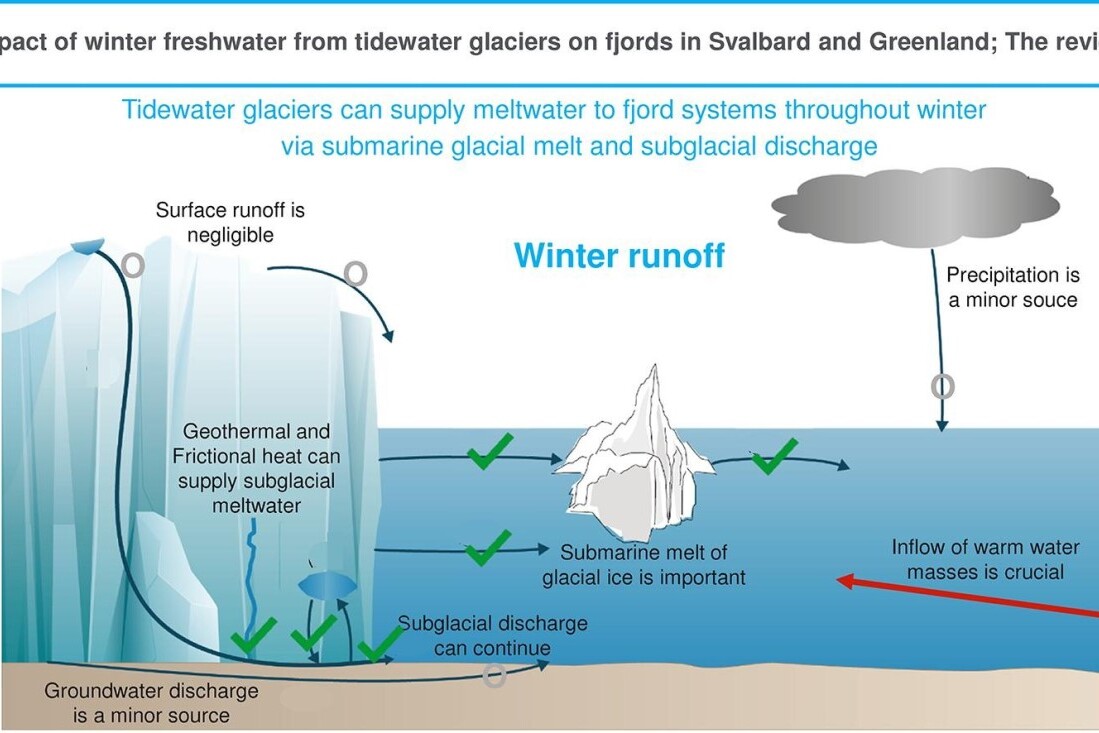
Impact of winter freshwater from tidewater glaciers on fjords in Svalbard and Greenland; A review
This review paper is the first to collect and synthesise the available knowledge, across various disciplines, on the importance of wintertime freshwater inflow from tidewater glaciers into Arctic fjords. While surface melt is limited during winter, tidewater glaciers can continue to deliver freshwater into the marine environment.
August 22, 2023
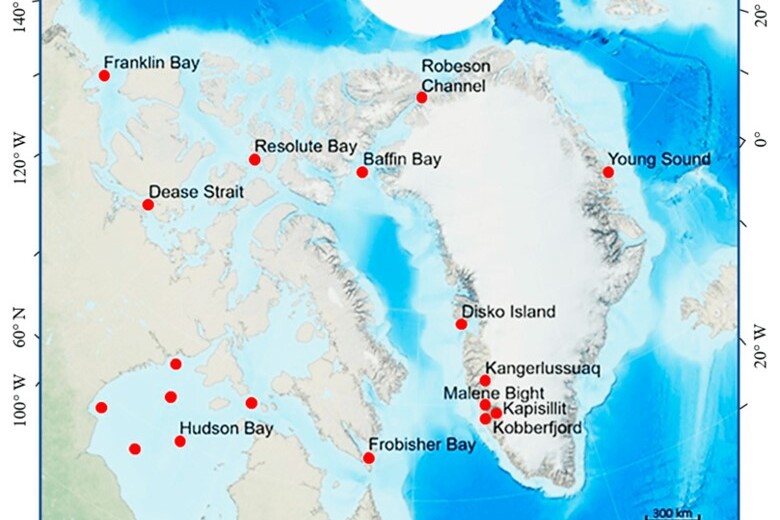
A dataset for investigating socio-ecological changes in Arctic fjords
The collection of in situ data is generally a costly process, with the Arctic being no exception. Indeed, there has been a perception that the Arctic is lacking in situ sampling; however, after many years of concerted effort and international collaboration, the Arctic is now rather well sampled, with many cruise expeditions every year.
July 6, 2023
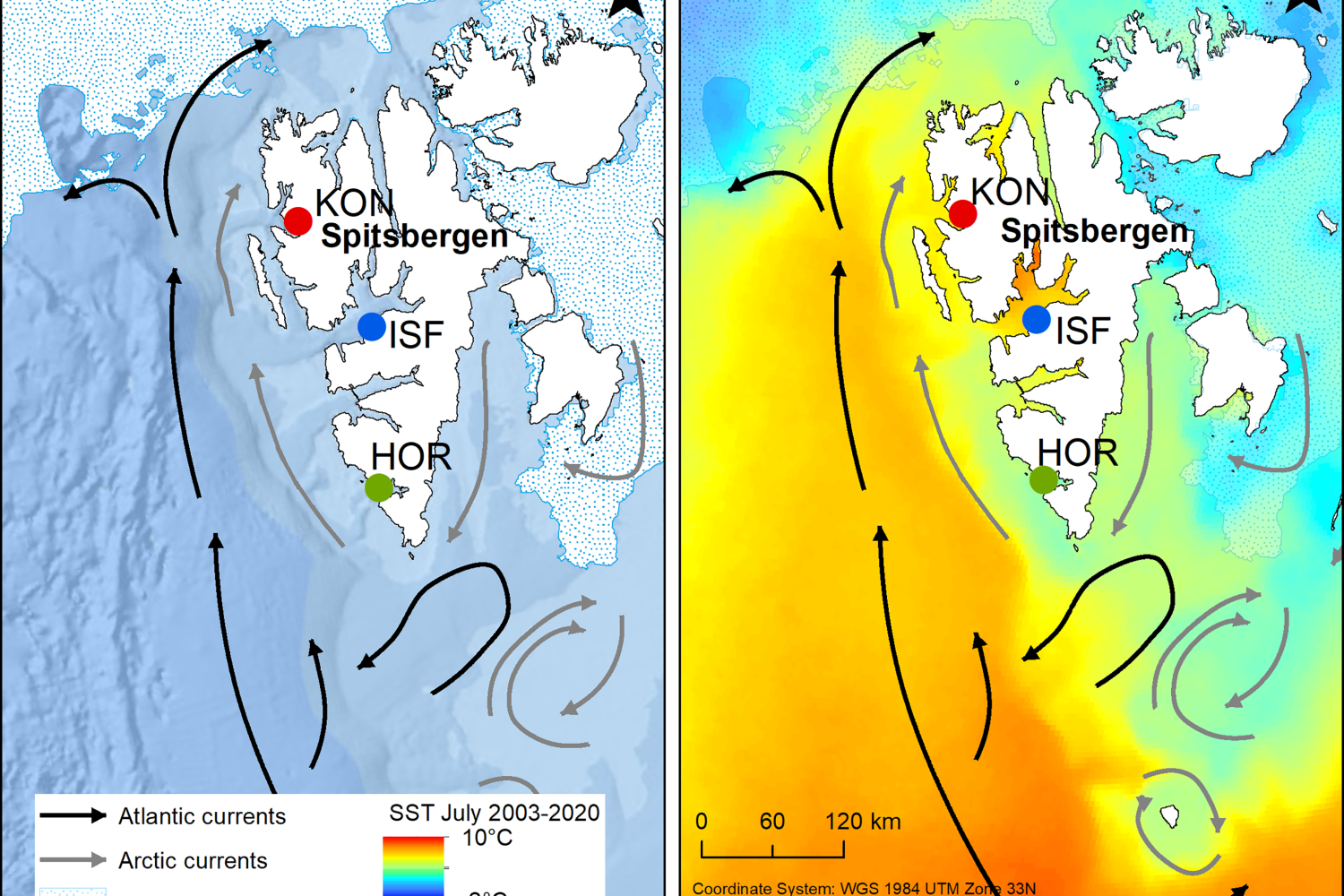
High-frequency, year-round time series of the carbonate chemistry in a high-Arctic fjord (Svalbard)
The Arctic Ocean is subject to high rates of ocean warming and acidification, with critical implications for marine organisms as well as ecosystems and the services they provide.
June 29, 2023
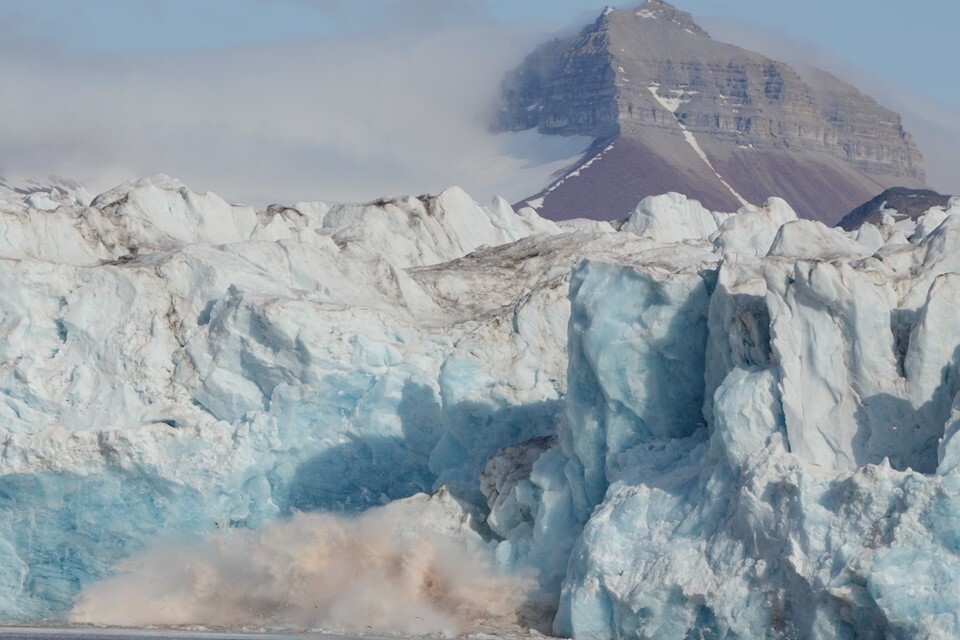
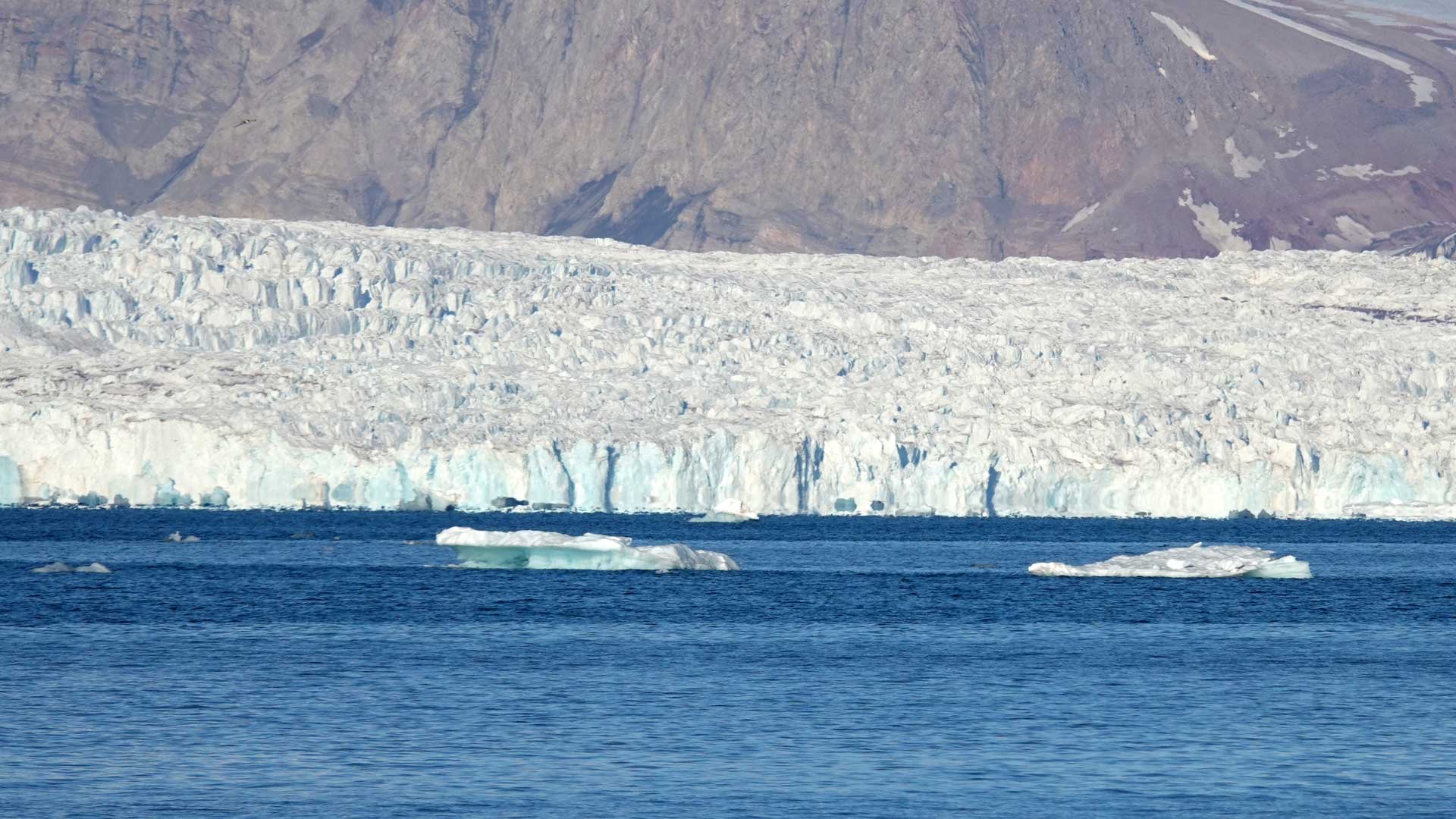
Glacier retreat alters downstream fjord ecosystem structure and function in Greenland
The melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet is accelerating, with glaciers shifting from marine to land termination and potential consequences for fjord ecosystems downstream.
June 16, 2023
A fjord with a land-terminating glacier: Meltwater, bio-optics, particulate matter, nutrients, phytoplankton species, and primary production in west Greenland
Land-terminating glaciers and submarine melting of marine-terminating glaciers are significant features in Arctic regions and are foreseen to become more frequent as marine-terminating glaciers ultimately develop into a land-terminated state.
June 13, 2023
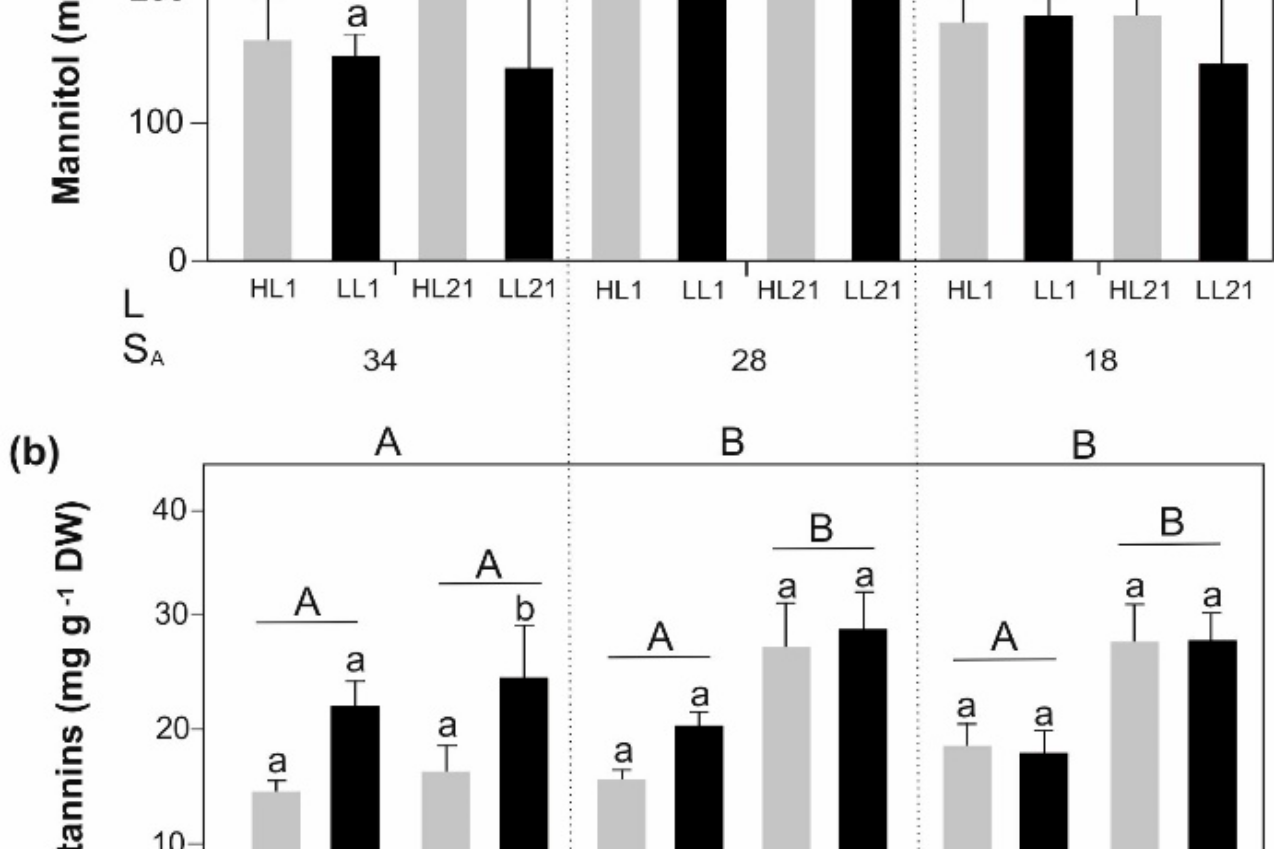
Exploring intraspecific variability – biochemical and morphological traits of the sugar kelp Saccharina latissima along latitudinal and salinity gradients in Europe
Broadly distributed seaweeds, such as the boreal-temperate kelp species Saccharina latissima, contain a multitude of metabolites supporting acclimation to environmental changes, such as temperature and salinity.
May 18, 2023
Coping with rapid and cascading changes in Svalbard: the case of nature-based tourism in Svalbard
Tourism has been booming in Svalbard and has almost returned to pre-pandemic levels. At the same time, the island is a hotspot of rapid and cascading climate and environmental changes, which are already placing natural and social systems under stress.
May 16, 2023
Ecological impacts of climate change on Arctic marine megafauna
Global warming affects the Arctic more than any other region. Mass media constantly relay apocalyptic visions of climate change threatening Arctic wildlife, especially emblematic megafauna such as polar bears, whales, and seabirds.
April 11, 2023
Effects of Arctic commercial shipping on environments and communities: context, governance, priorities
Increasing shipping traffic in the Arctic Ocean creates an emerging need to understand the consequences of maritime operations on the Arctic environment and coastal Indigenous and non-Indigenous communities, as well as potential governance responses. To address this need, we examine recent shipping trends and assess their impact on Arctic environments and communities.
April 11, 2023
Demographic responses of Arctic seabirds to spring sea-ice variations
The Arctic experiences a rapid retreat of sea-ice, particularly in spring and summer, which may dramatically affect pagophilic species. In recent years, the decline of many Arctic seabird populations has raised concerns about the potential role of sea-ice habitats on their demography.
February 22, 2023
Managing Svalbard Tourism: Inconsistencies and Conflicts of Interest
The Svalbard Archipelago has experienced a rapid increase in tourism-related activities over the past few decades. The Norwegian Government’s ambition to develop the Archipelago’s tourism industry offers multiple socio-economic opportunities.
February 1, 2023
Glacial retreat and rising temperatures are limiting the expansion of temperate kelp species in the future Arctic
Kelps act as ecosystem engineers on many polar rocky shore coastlines. The underwater light climate and temperature are the main drivers for their vertical and latitudinal distribution. With temperatures rising globally, an Arctic expansion of temperate kelp species and an accelerating glacial melt is predicted.
January 13, 2023
Drivers of Change in Arctic Fjord Socio-ecological Systems: Examples from the European Arctic
Fjord systems are transition zones between land and sea, resulting in complex and dynamic environments. They are of particular interest in the Arctic as they harbour ecosystems inhabited by a rich range of species and provide many societal benefits. The key drivers of change in European Arctic (i.e. Greenland, Svalbard, and Northern Norway) fjord socioecological systems are reviewed here, ...
December 28, 2022
To Live Up to Our Name “Greenland”: Politics of Comparison in Greenland’s Green Transition
In 2021, the Government of Greenland made an active, discursive shift in the political discourse regarding Greenlandic development. Since the last general election, the political agenda has changed from prioritizing industrialization and the development of extractive industries (with little focus on ratifying international treaties and commitments to lower CO2 emissions to limit global warming) to suddenly wanting to “live up to our name, Greenland” by kickstarting a green transition with the ambition to be an exporter of hydropower and mining rare earth elements (REE) to support the technology for the green transition.
December 19, 2022
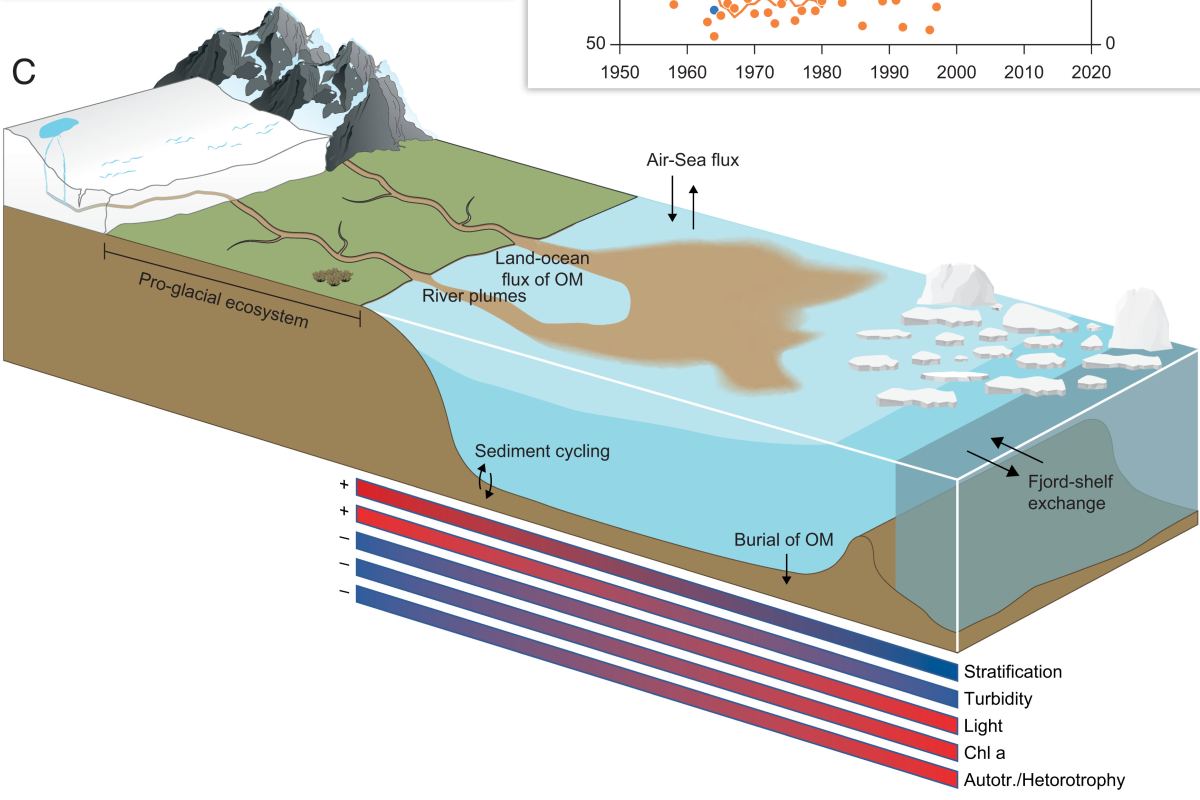
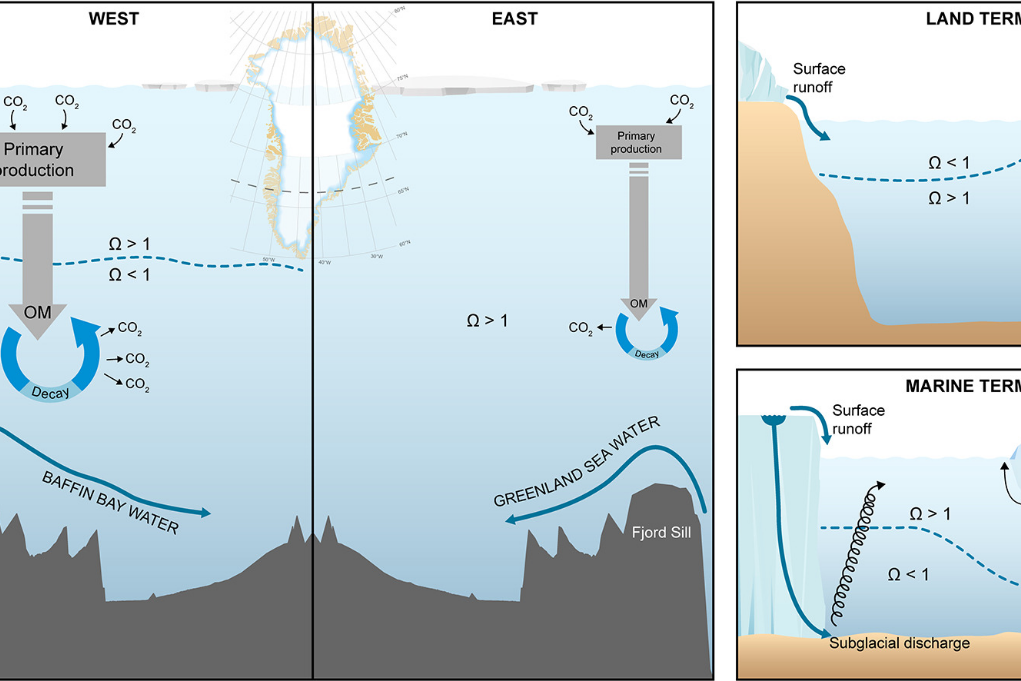
Glacial meltwater determines the balance between autotrophic and heterotrophic processes in a Greenland fjord
Global warming accelerates melting of glaciers and increases the supply of meltwater and associated inorganic particles, nutrients, and organic matter to adjacent coastal seas, but the ecosystem impact is poorly resolved and quantified.
November 9, 2022
Impact of climate change on Arctic macroalgal communities
The Arctic region faces a warming rate that is more than twice the global average. Sea-ice loss, increase in precipitation and freshwater discharge, changes in underwater light, and amplification of ocean acidification modify benthic habitats and the communities they host.
October 13, 2022
High Ecophysiological Plasticity of Desmarestia aculeata (Phaeophyceae) Present in an Arctic Fjord under Varying Salinity and Irradiance Conditions
The seaweed Desmarestia aculeata (Phaeophyceae) is distributed in the temperate zone of the North Atlantic up to the Arctic, where it is exposed to a high Arctic light regime and fluctuating salinity conditions resulting from glacial and terrestrial run-off. Information on how this species is able to thrive under current and future Arctic conditions is scarce.
September 30, 2022
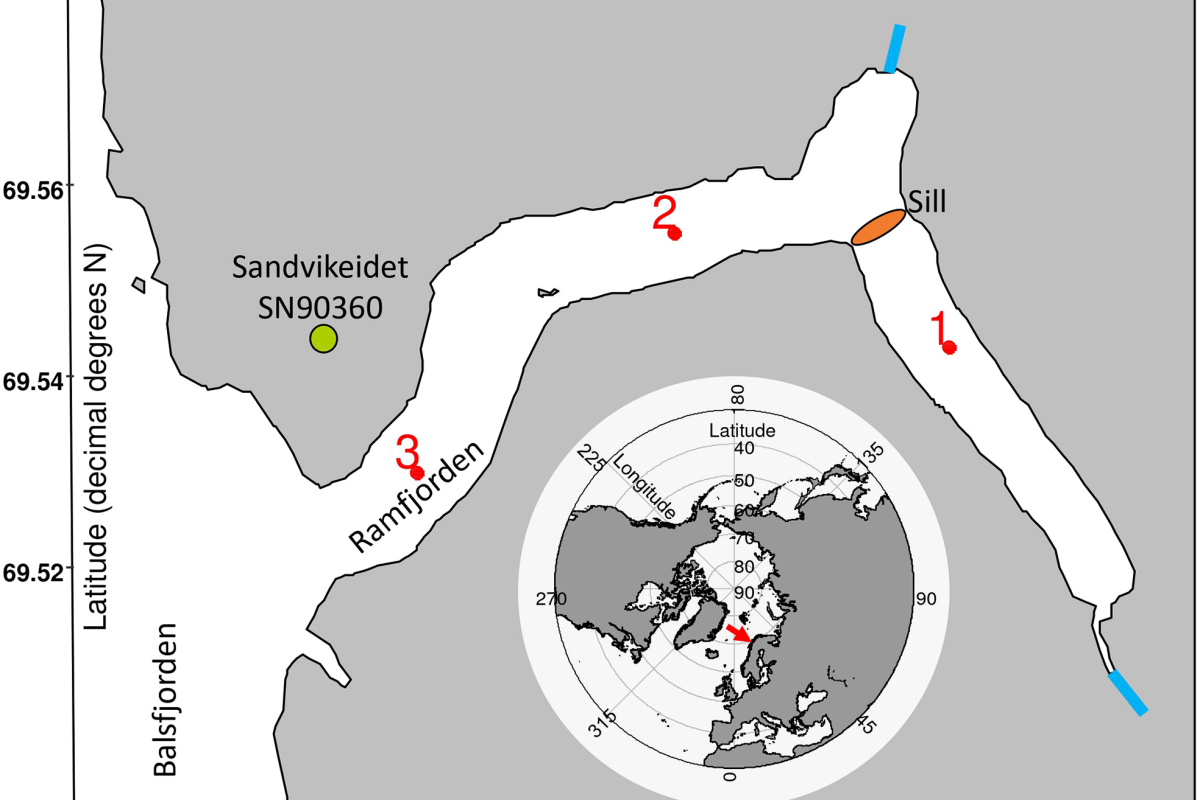
Light and freshwater discharge drive the biogeochemistry and microbial ecology in a sub-Arctic fjord over the Polar night
The polar night has recently received increased attention as a surprisingly active biological season. Yet, polar night microbial ecology is a vastly understudied field. To identify the physical and biogeochemical parameters driving microbial activity over the dark season, we studied a sub-Arctic fjord system in northern Norway from autumn to early spring with detailed monthly sampling.
September 26, 2022
Coastal freshening drives acidification state in Greenland fjords
Greenland’s fjords and coastal waters are highly productive and sustain important fisheries. However, retreating glaciers and increasing meltwater are changing fjord circulation and biogeochemistry, which may threaten future productivity. The freshening of Greenland fjords caused by unprecedented melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet may alter carbonate chemistry in coastal waters, influencing CO2 uptake and causing biological consequences from acidification.
September 14, 2022
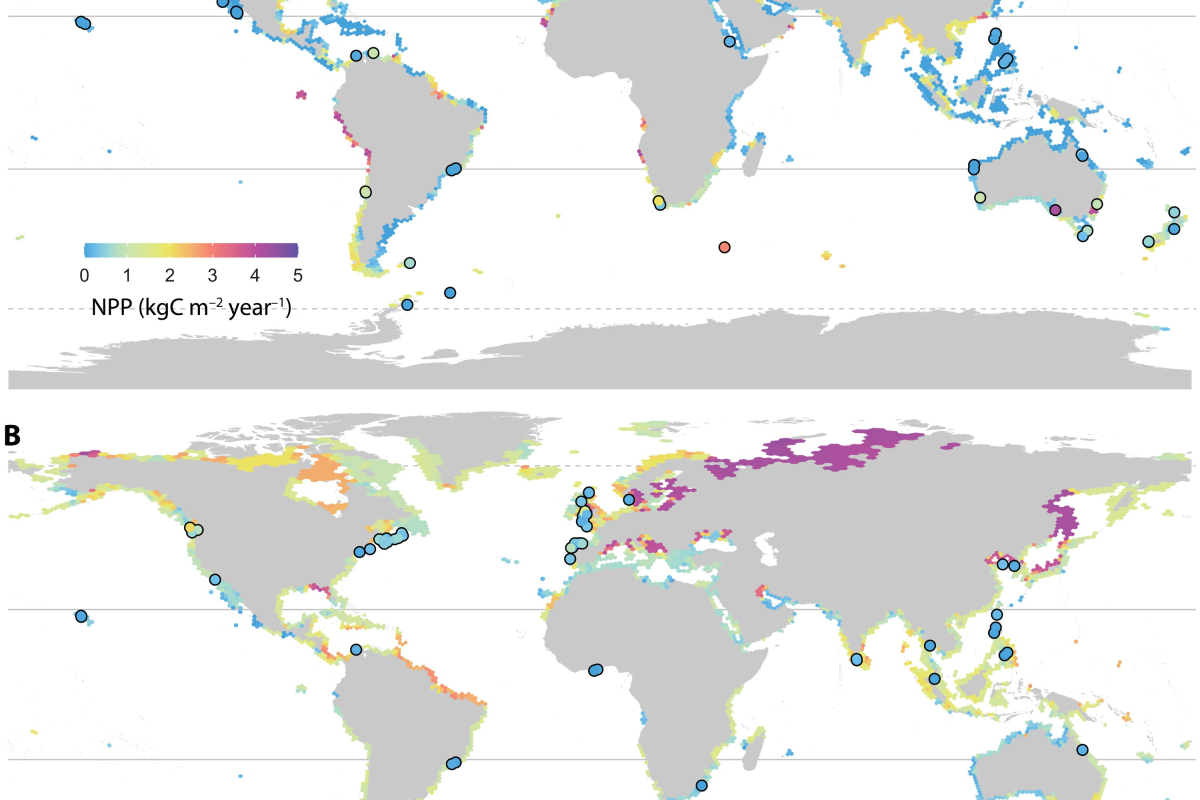
Global seaweed productivity
The magnitude and distribution of net primary production (NPP) in the coastal ocean remains poorly constrained, particularly for shallow marine vegetation. Here, using a compilation of in situ annual NPP measurements across >400 sites in 72 geographic ecoregions, we provide global predictions of the productivity of seaweed habitats, which form the largest vegetated coastal biome on the planet.
August 11, 2022
Seasonal mesozooplankton patterns and timing of life history events in high-arctic fjord environments
Seasonal patterns in mesozooplankton composition, vertical distribution, and timing of reproduction are challenging to study in the open sea due to ocean currents and mix of populations of different origins. Sill fjords, on the other hand, with restricted water exchange, are ideal locations for studying taxa- and community-specific adaptations to the prevailing environment.
July 25, 2022
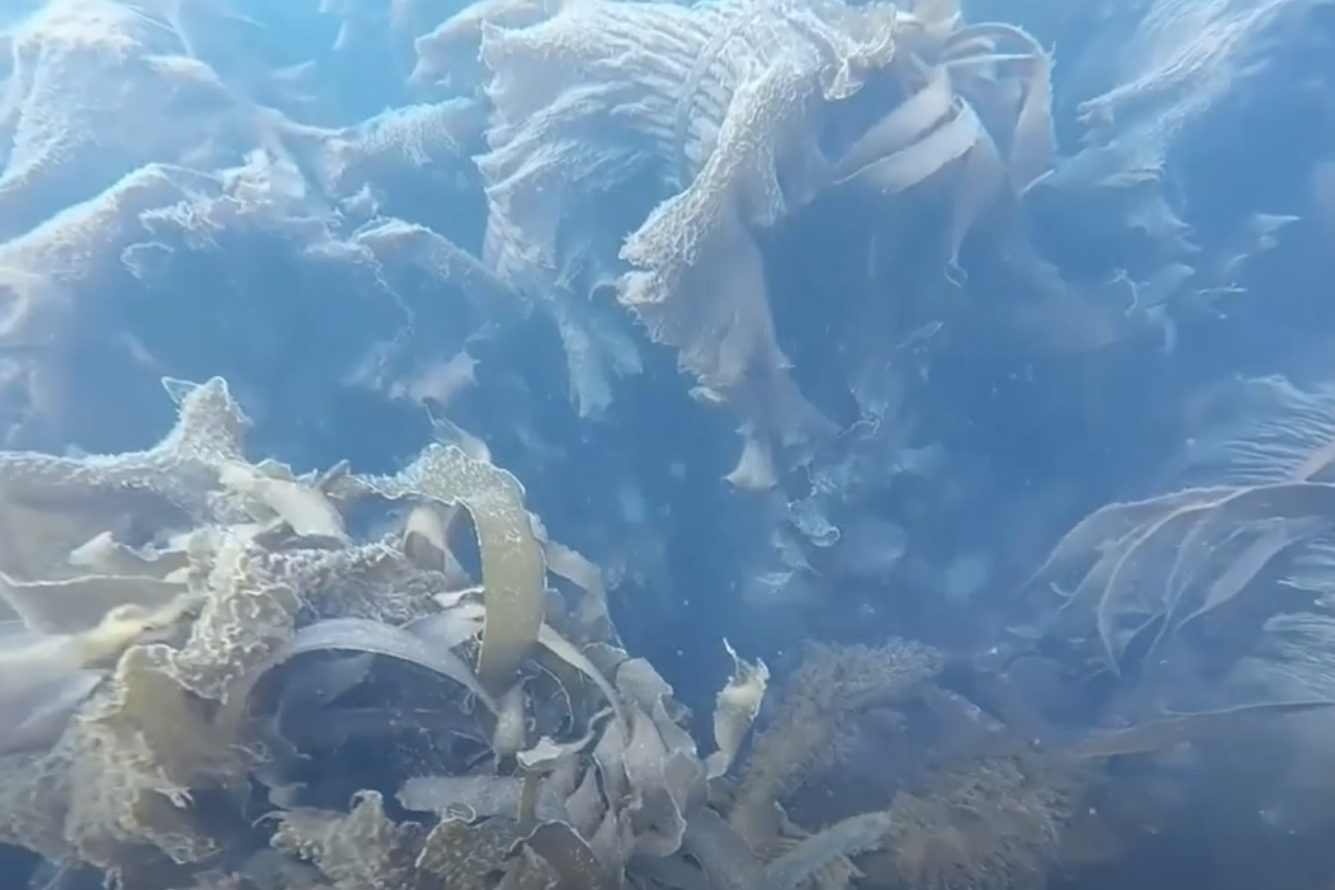
Video survey of deep benthic macroalgae and macroalgal detritus along a glacial Arctic fjord: Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen)
In Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen), we quantified the zonation of visually dominant macroalgal taxa and of detached macroalgae from underwater videos taken in summer 2009 at six transects between 2 and 138 m water depth. For the first time, we provide information on the occurrence of deep water red algae below the kelp forest and of detached macroalgae at water depth > 30 m.
June 20, 2022
Consequences of Atlantification on a Zooplanktivorous Arctic Seabird
Global warming, combined with an increasing influence of Atlantic Waters in the European Arctic, are causing a so-called Atlantification of the Arctic. This phenomenon is affecting the plankton biomass and communities with potential consequences for the upper trophic levels. Using long-term data (2005-2020) from a high Arctic zooplanktivorous seabird, the little auk (Alle alle), we tested the hypothesis that the Atlantification affects its diet, body condition and demography.
June 15, 2022
Kelp Forest Distribution in the Nordic Region
Kelp forests are productive coastal ecosystems that provide a range of ecosystem services. Mapping the distribution and area occupied by kelp forests is a critical step to identify their ecosystem functions and services, including their role in the carbon cycle, and to detect changes in their distribution.
June 9, 2022
Implementation and evaluation of open boundary conditions for sea ice in a regional coupled ocean (ROMS) and sea ice (CICE) modeling system
The Los Alamos Sea Ice Model (CICE) is used by several Earth system models where sea ice boundary conditions are not necessary, given their global scope. However, regional and local implementations of sea ice models require boundary conditions describing the time changes of the sea ice and snow being exchanged across the boundaries of the model domain.
May 11, 2022
Advancements of sustainable development goals in co-production for climate change adaptation research
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a new discursive regime that encompasses global environmental change challenges and sustainability sciences, including adaptation to climate change. Co-production of knowledge has become a key, intrinsic component in both sustainability sciences and adaptation research.
May 1, 2022
Hyposalinity affects diurnal photoacclimation patterns in the rhodophyte Palmaria palmata under mimicked Arctic summer conditions
Ocean temperatures have increased during 2011–2020, causing significant changes in the marine environment. One area that has been affected by the temperature increase is the Arctic, leading to a decrease in glacial mass and an increase in meltwater. Some organisms e.g., Fucus (brown seaweed) benefit from these environmental changes while others may be strongly affected.
April 12, 2022
Highly Productive Ice Algal Mats in Arctic Melt Ponds: Primary Production and Carbon Turnover
Arctic summer sea ice extent is decreasing and thinning, forming melt ponds that cover more than 50% of the sea ice area during the peak of the melting season. Despite of this, ice algal communities in melt ponds are understudied and so are their contribution to the Arctic Ocean primary production and carbon turnover.
March 3, 2022
Fish Assemblages of a Sub-Arctic Fjord Show Early Signals of Climate Change Response Contrary to the Benthic Assemblages
Arctic benthic ecosystems are facing high-speed environmental changes, such as decreased sea ice coverage, increased temperature and precipitations, as well as the invasion by non-indigenous species. Few sub-arctic fjords have the particularity to have an inner-most part forming a basin in which water remains very cold.
March 1, 2022
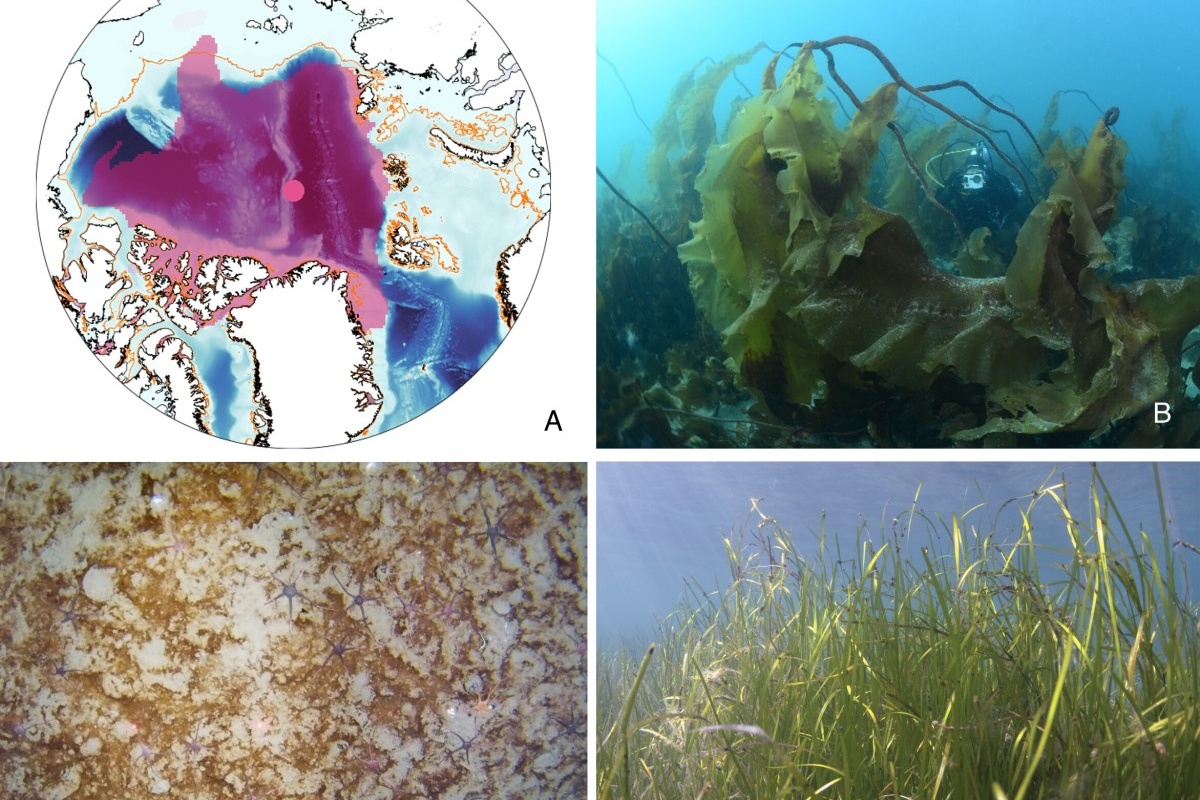
Major Expansion of Marine Forests in a Warmer Arctic
Accelerating warming and associated loss of sea ice are expected to promote the expansion of coastal marine forests (macrophytes) along the massive Arctic coastlines. Yet, this region has received much less attention compared to other global oceans. The available future projections of Arctic macrophytes are still limited to few species and regions, and mostly focused at lower latitude ranges, thus precluding well-informed IPCC impact assessments, conservation and management.
January 31, 2022
The importance of turbulent ocean–sea ice nutrient exchanges for simulation of ice algal biomass and production with CICE6.1 and Icepack 1.2
Different sea ice models apply unique approaches in the computation of nutrient diffusion between the ocean and the ice bottom, which are generally decoupled from the calculation of turbulent heat flux.
January 25, 2022
Cetacean spatial trends from 2005 to 2019 in Svalbard, Norway
This study uses cetacean sighting data, acquired via a citizen science programme, to update distributions and spatial trends of whales and dolphins in waters around the Svalbard Archipelago during the period 2005–2019.
December 21, 2021
Differential acclimation responses to irradiance and temperature in two co-occurring seaweed species in Arctic fjords
Arctic fjord systems experience large amplitudes of change in temperature and radiation regime due to climate warming and the related decrease in sea ice. The resultant increase in irradiance entering the water column influences photosynthetic activity of benthic and pelagic primary producers.
October 11, 2021
Summer Heatwave Impacts on the European Kelp Saccharina latissima Across Its Latitudinal Distribution Gradient
Kelps are important foundation species in coastal ecosystems currently experiencing pronounced shifts in their distribution patterns caused by ocean warming. While some populations found at species’ warm distribution edges have been recently observed to decline, expansions of some species have been recorded at their cold distribution edges.
August 1, 2021
Towards a Unifying Pan-Arctic Perspective of the Contemporary and Future Arctic Ocean
Since 2002 the pan-arctic integration symposia has attempted to figure out how the Arctic Ocean can be understood as an independent, mediterranean type ocean and node of the Northern Hemisphere.
July 30, 2021
Upwelling Irradiance below Sea Ice—PAR Intensities and Spectral Distributions
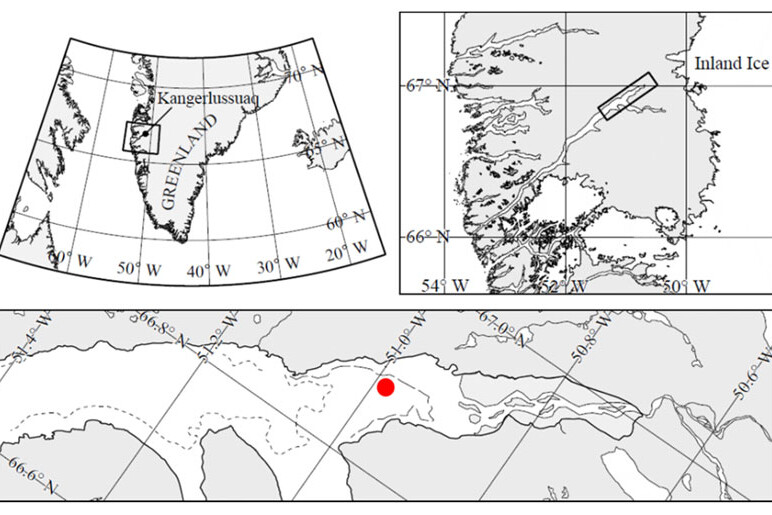
Snow cover on sea ice is the most important factor controlling light availability for sea ice algae, but it is predicted by climate models to become more variable and stochastic. Here, we document effects of a sudden, complete loss of the entire snow cover on first-year sea ice at Kangerlussuaq Fjord, West Greenland, due to a natural Föhn wind event that caused a ca. 17 °C air temperature increase over 36 h.
July 27, 2021
Photobiological Effects on Ice Algae of a Rapid Whole-Fjord Loss of Snow Cover during Spring Growth in Kangerlussuaq, a West Greenland Fjord
Snow cover on sea ice is the most important factor controlling light availability for sea ice algae, but it is predicted by climate models to become more variable and stochastic. Here, we document effects of a sudden, complete loss of the entire snow cover on first-year sea ice at Kangerlussuaq Fjord, West Greenland, due to a natural Föhn wind event that caused a ca. 17 °C air temperature increase over 36 h.
July 22, 2021
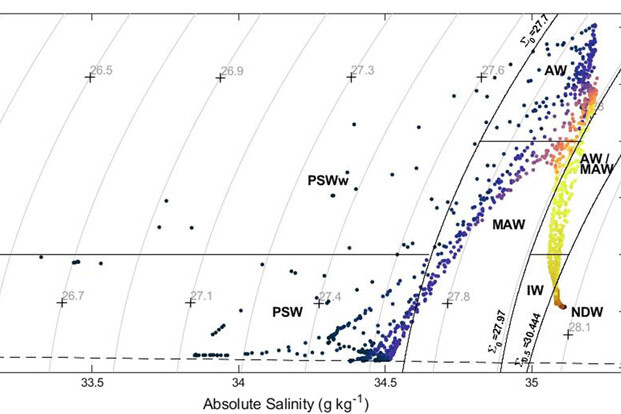
Nutrients in Water Masses in the Atlantic Sector of the Arctic Ocean: Temporal Trends, Mixing and Links With Primary Production
There is strong evidence of an increase in primary production (PP) in the Arctic Ocean (AO) over the last two decades. Further increases will depend on the interplay between decreasing light limitation for primary producers, as the sea ice extent and thickness decrease
June 18, 2021
Editorial: Towards a Unifying Pan-Arctic Perspective of the Contemporary and Future Arctic Ocean
An international symposium addressing pan-Arctic perspectives of the marine ecosystems of the Arctic Ocean took place in October 2017 and this editorial introduces the publications that derived from the conference.
May 17, 2021
Bearded seal (Erignathus barbatus) vocalizations across seasons and habitat types in Svalbard, Norway
Male bearded seals (Erignathus barbatus) use vocal displays to attract females and to compete with other males during the mating season. This makes it possible to monitor breeding populations of this species using passive acoustic monitoring (PAM).
March 13, 2021
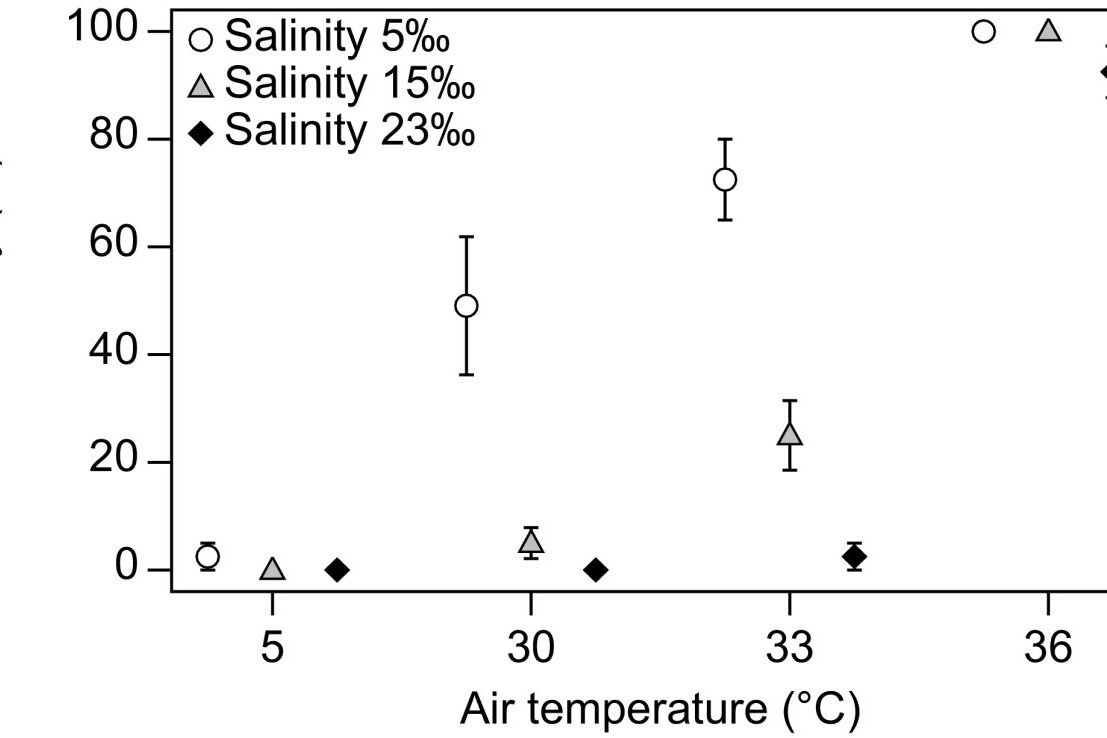
Freshening increases the susceptibility to heat stress in intertidal mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the Arctic
Temperatures in the Arctic are increasing at a faster pace than at lower latitudes resulting in range expansion of boreal species. In Greenland, the warming also drives accelerating melt of the Greenland Ice Sheet resulting in more meltwater entering Greenland fjords in summer.
February 4, 2021
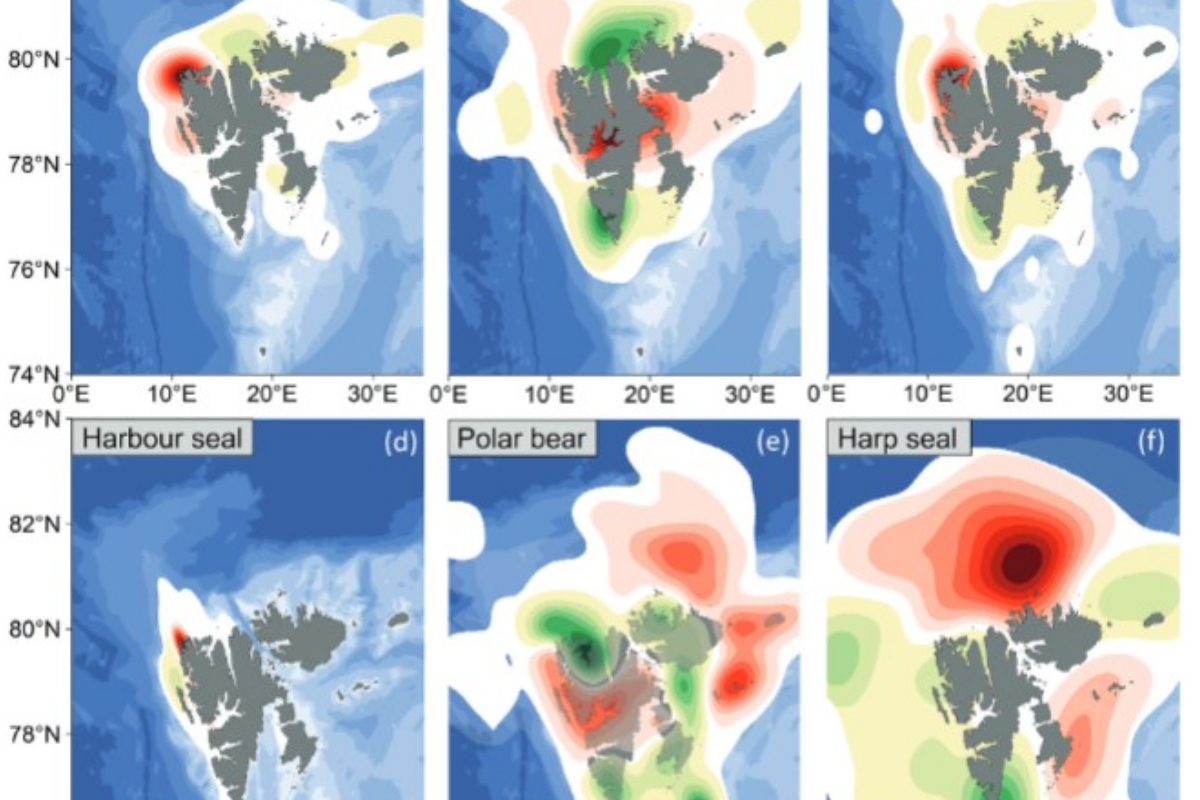
Distribution and habitat characteristics of pinnipeds and polar bears in the Svalbard Archipelago, 2005–2018
This study presents comprehensive mapping of the current distribution of pinnipeds and polar bears (Ursus maritimus) around Svalbard based on a regional marine mammal sightings programme and explores time-trends (2005–2018).
December 28, 2020
Systemer i et klimaforandret Arktis
Systemer i et klimaforandret Arktis: Den svære dialog mellem fakta- og meningsproducenter.
December 23, 2020
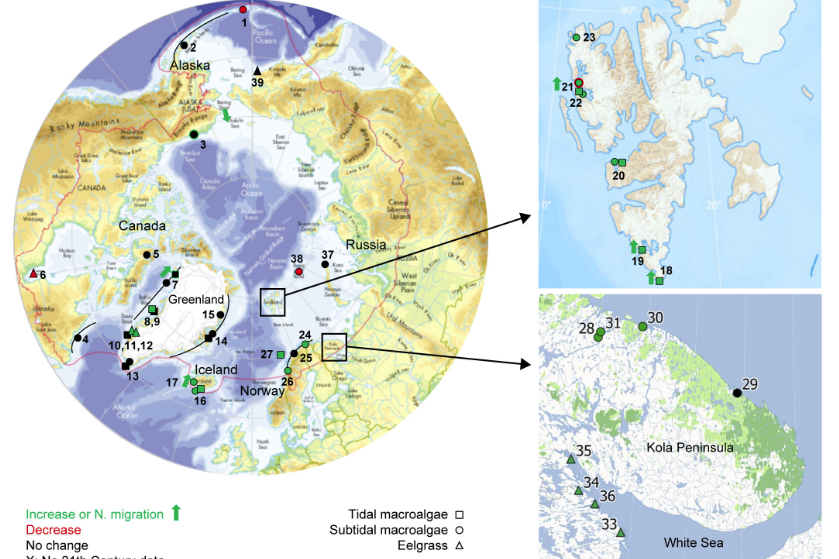
Imprint of Climate Change on Pan-Arctic Marine Vegetation
The Arctic climate is changing rapidly. The warming and resultant longer open water periods suggest potential for expansion of marine vegetation along the vast Arctic coastline. We compiled and reviewed the scattered time series on Arctic marine vegetation and explored trends for macroalgae and eelgrass (Zostera marina).
CONFERENCES
Communication and networking are important! Thus, FACE-IT participated in scientific conferences worldwide. Here you can find all conferences where FACE-IT is involved with presentations, sessions, or as co-organising project.
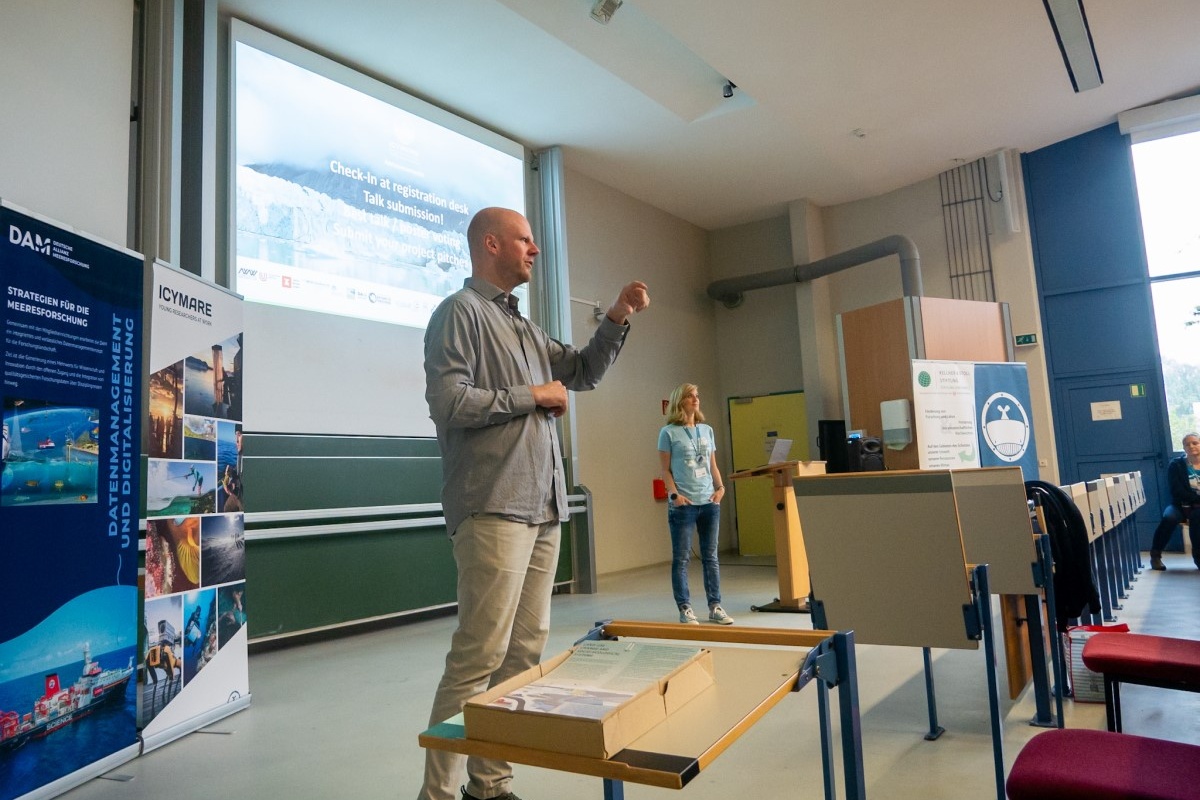
Conference from 16 to 20 September 2024
FACE-IT keynote lecture and poster exhibition at ICYMARE 2024 BREMEN
Conference from 16 to 21 June 2024
FACE-IT contributions to the World Biodiversity Forum 2024 in Davos, Switzerland
Conference from 14 to 15 May 2024
The 2024 EU Arctic Forum, Indigenous Peoples’ Dialogue and EU-Arctic Youth Dialogues
Conference from 07 to 08 May 2024
Arctic Biodiversity Session at the Arctic Circle Berlin Forum
Conference from 22 to 24 November 2023
FACE-IT attending workshop of the European Commission and the European Space Agency
Conference from 06 to 09 November 2023
FACE-IT colleagues contributing to the Nansen Legacy Symposium
Conference from 31 October to 01 November 2023
FACE-IT at the Svalbard Science Conference 2023
Conference from 17 to 24 February 2023.
Successful FACE-IT contributions at the Arctic Science Summit Week (ASSW) 2023
EXPEDITIONS
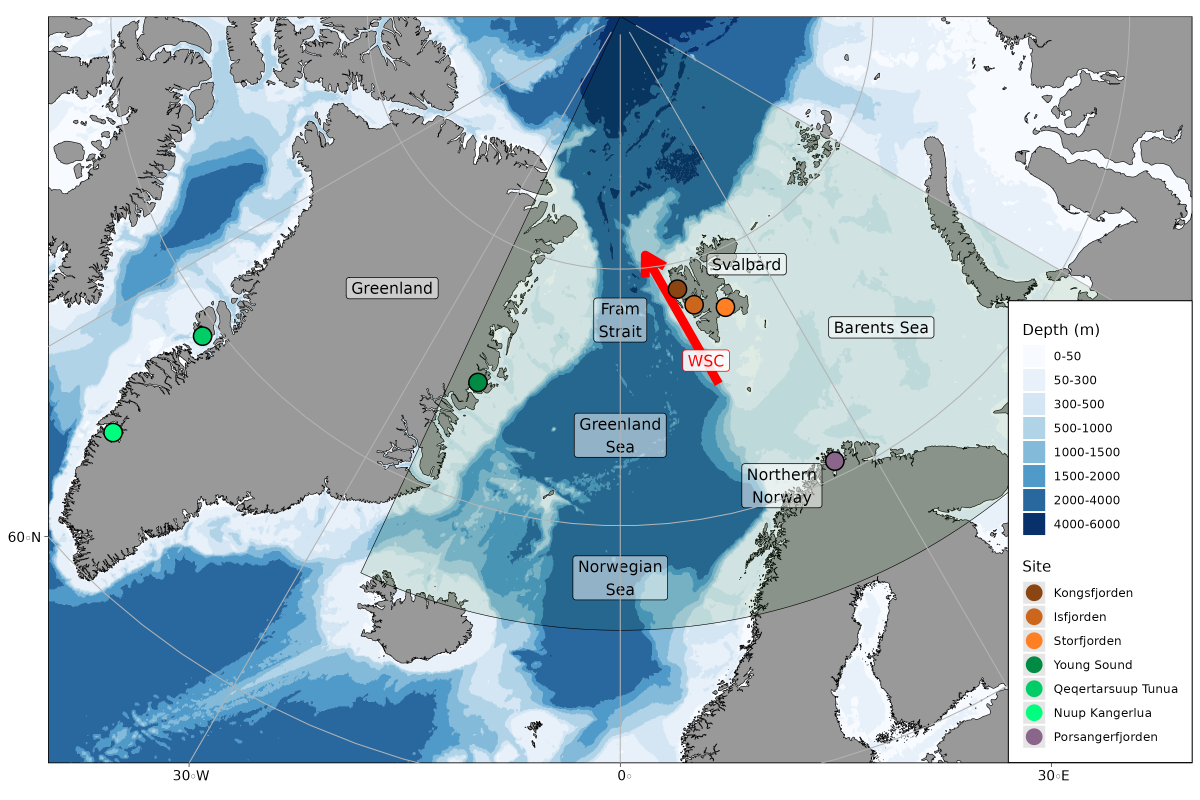
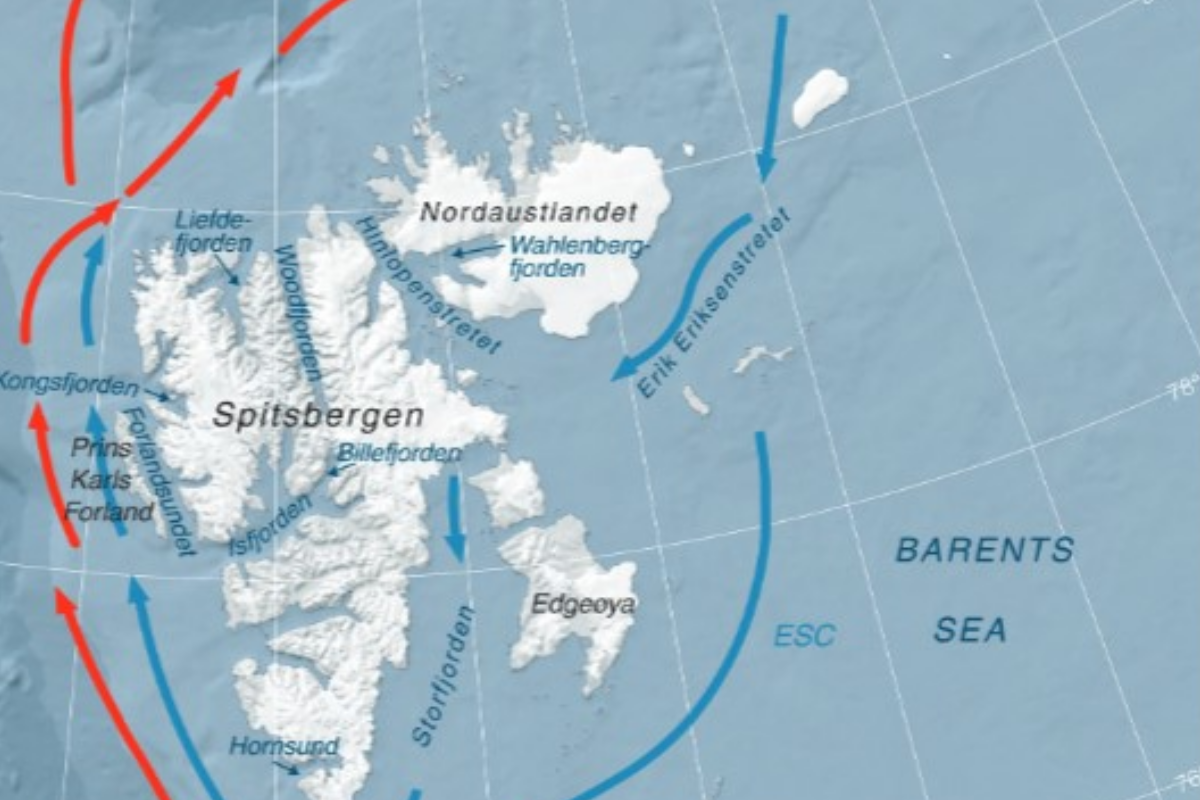
FACE-IT works in seven different Arctic fjords: Godthåbsfjord, Disko Bay, and Young Sound in Greenland; Kongsfjorden, Isfjorden, and Inglefieldbukta/Storfjorden in Svalbard; as well as Porsangerfjorden in Finnmark, Norway.
Check out the news on the FACE-IT expeditions!
September 1, 2023
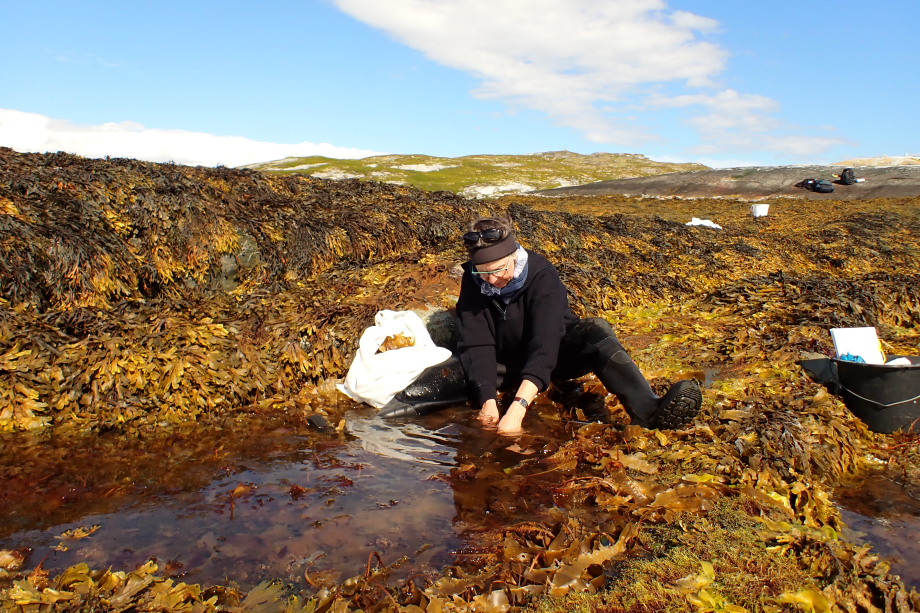
Population development and ecophysiology of the sea urchins Strongylocentrotus sp. in Porsangerfjorden, Finnmark, Norway
In August 2023, three researchers of the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) and the University of Bremen visited the Holmfjorden Research Station of the Norwegian Instutute of Marine Research (IMR). Marie Koch (AWI) and Simon Jungblut (Uni Bremen) had…
July 17, 2023
Future kelp forest communities on Greenland
Nora Diehl and Sarina Niedzwiedz from the University of Bremen conducted a field work campaign in Nuuk, Greenland in June / July 2023 to answer the question, how future Arctic kelp forest communities might look like. Kelps are brown macroalgae that…
May 15, 2023
Status of Arctic kelp forests around Svalbard
The Arctic and Svalbard in particular is warming at a rate far beyond the global average, leading to a reduction of sea-ice and glacial retreat. Fjords in Svalbard represent model systems to study climate change induced ecosystem transitions, as…
May 15, 2023
Influence of terrestrial run-off on kelp elemental composition and associated microbial community
End of August 2022, Sarina Niedzwiedz from the University of Bremen conducted a field campaign to analyse the effect of terrestrial run-off on Arctic kelp ecosystems. Kelps act as ecosystem engineers and foundation species, thereby providing the…
July 28, 2022
Adaptation and acclimation processes of Arctic seaweeds and macrozoobenthos of Porsangerfjorden
In summer 2022, a group of scientists of the University of Bremen and the Alfred Wegener Institute investigated the biochemical capacities and reactions to changing temperatures in benthic key species of the Porsangerfjord. We stayed at the…
July 26, 2022
Biodiversity and biomass of the intertidal and shallow subtidal seaweeds of Porsangerfjorden
In summer 2022, a team of 4 scientists specialized on seaweeds (from Germany, Norway and Canada) undertook an expedition to the Holmfjorden Research Station of the Norwegian Institute for Marine Research at the Porsangerfjord. Over a time period of…
December 1, 2021
Cryosphere reduction and related shifts in Arctic biodiversity
The Ny-Ålesund research station has a long tradition in international and interdisciplinary research cooperation, which has been fostered by the ever-increasing interaction within and between the four flagship programs operated by NySMaC. One…
WORKSHOPS
Stakeholders and rightholders will be involved in the co-producing of knowledge within the FACE-IT project. Here, you will find information on the respective workshops and involvements.
June 16, 2024
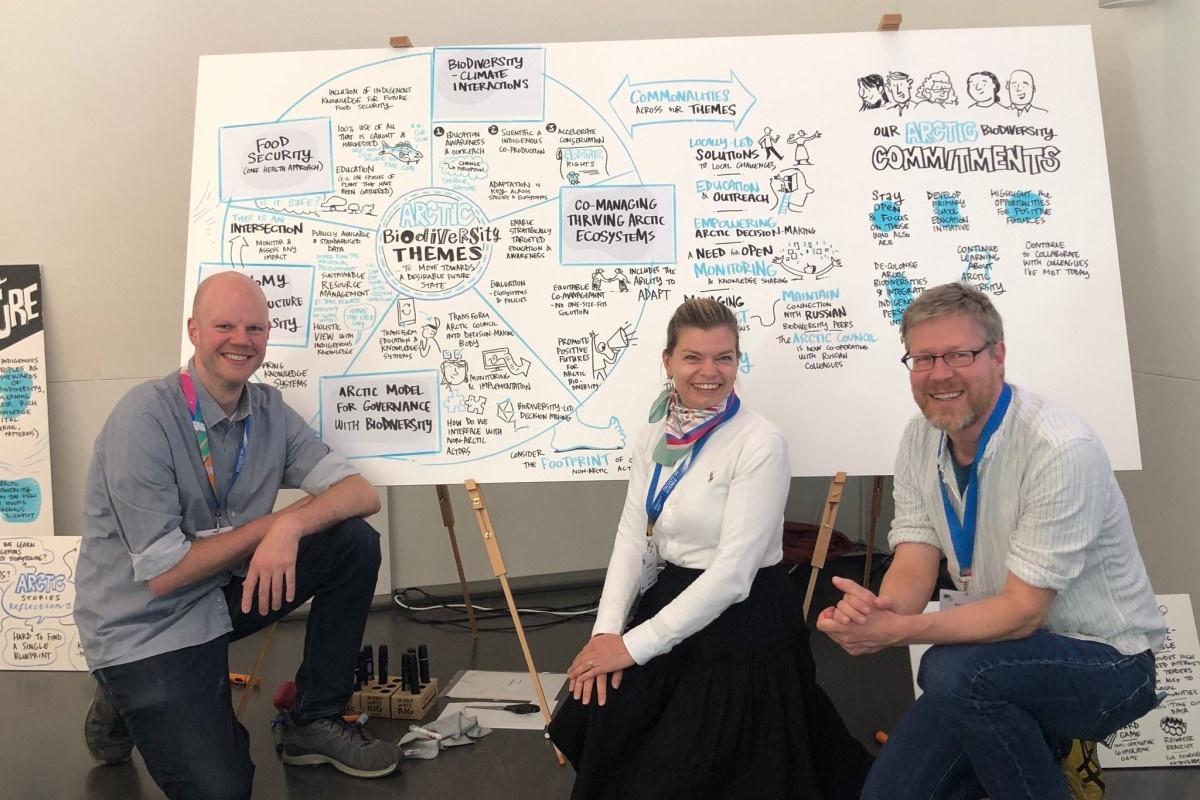
Desirable futures for Arctic biodiversity: FACE-IT contributed insights from coastal environmental economics
In the frame of the World Biodiversity Forum 2024 in Davos, Switzerland, the FACE-IT managing team Kai Bischof and Simon Jungblut (University of Bremen) as well as Julia Olsen (Nord University) engaged in a workshop in the desirable futures for…
May 29, 2024
FACE-IT joins workshop of the Svalbard Social Science Initiative
In the frame of the Arctic Congress in Bodø (29 May - 03 June 2024), the Svalbard Social Science Initiative SSSI organized the second of a series of workshops entitled “Building transdisciplinary bridges for sustainable Svalbard and Arctic…
April 17, 2024
FACE-IT workshop on management options to mitigate climate change effects in Lakselv, Finnmark
On 08 April 2024, FACE-IT and the collaborating project "Future Arctic Lives" invited for a workshop on Lakselv, Porsanger, Finmark. This workshop explored the lokal management options for the mitigation of climate and environmental changes. 15…
January 16, 2024
FACE-IT co-organized workshops in Porsanger, Finnmark
The FACE-IT colleagues Camilla Risvoll and Solveig Øye Bjørdal from the Nordland Research Institute co-organized a set of workshops in the Posanger Municipality, Finnmark, Norway.
November 17, 2023
First biennial Greenland Marine Research Seminar co-organized by FACE-IT
The first biennial Greenland Marine Research Seminar hosted by the Greenland Institute of Natural Resources (GINR) brought together the Davis Strait Observing System as well as the FACE-IT and ECOTIP projects with stakeholders, managers, and…
November 17, 2023
Sustainable Arctic cruise tourism workshop co-organized by FACE-IT
"How is cruise tourism developing in Greenland and how to secure the balancing of interests and concerns of businesses and communities in a fragile environment?" This was the topic of a seminar organized by the FACE-IT project together with the…
November 2, 2023
Invitation: Workshop on sustainable Arctic cruise tourism development in Nuuk, Greenland
“Cruise trouble”: How to sustainably develop Arctic cruise tourism? Join our seminar to learn about how different Arctic destinations cope with cruise tourism and how cruise tourism impacts communities and the environment. Share your views on…
September 1, 2023
Invitation to Greenland Marine Research Seminar
The Greenland Institute of Natural Resources (GINR), partner in the FACE-IT project, invites to a Greenland Marine Research Seminar in the frame of the Greenland Science Week Nuuk (6-10 November 2023). The seminar will take place on 7 November 2023,…
April 20, 2023
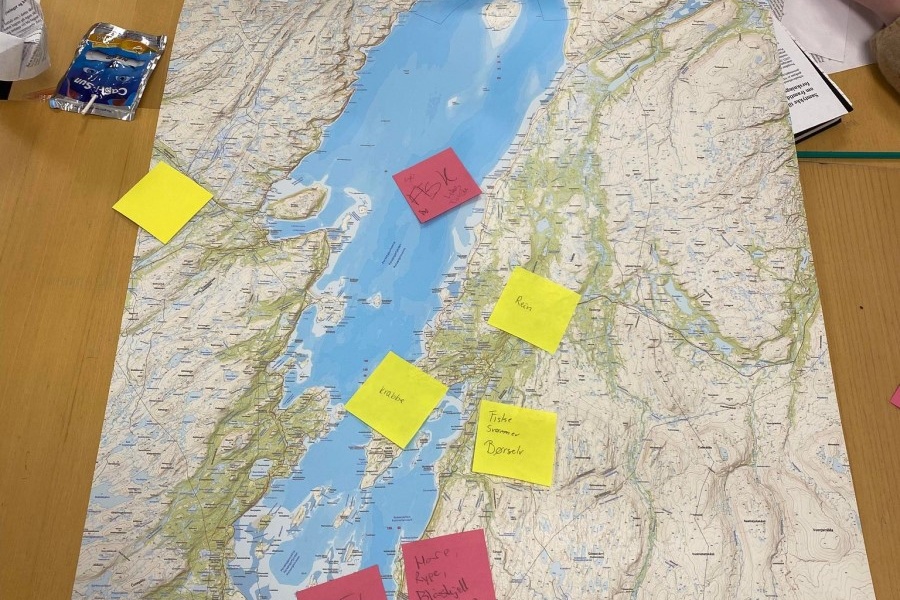
FACE-IT Workshop on the future Porsangerfjord, Nordkapp
FACE-IT, the project Future Arctic Lives and the Porsanger Municipality invited to a workshop about the future Porsangerfjorden from the stake- and rightholders point of view! On 03 and 04 May, fishermen, young people and others from the…
October 23, 2022
FACE-IT Scenario Workshop in Longyearbyen, Svalbard
On 25 October 2022, FACE-IT in collaboration with the BalancingAct project (funded by the Research Council of Norway), will be hosting a scenario workshop in Longyearbyen, Svalbard. Stakeholders of the tourism industry in Svalbard will explore the…
June 15, 2022
FACE-IT Scenario Workshop in Nuuk, Greenland
On 26 August 2022, FACE-IT will be hosting a scenario workshop in Nuuk, Greenland, inviting stakeholders of the Nuup Kangerlua fjord to explore how climate change and other factors might affect the fjord and its future value for fishing and…
PUBLIC EVENTS
The project engages in public events and organizes lectures or colloquia for the interested public. Check out the possibilities to get in touch with FACE-IT scientists!
[in German] Public lectures in the House of Science Bremen
Wälder unter Wasser – Großalgen und ihre Gemeinschaften
Public Colloquium: 30 November 2022
Arctic fjords without ice? Biological and societal effects of melting glaciers
Public Colloquium: 25 November 2020