Arctic fjords are social-ecological systems
Glacier fronts and sea ice systems are hotspots of biodiversity. Their retreat will pose threats to Arctic coastal ecosystem function and eventually local livelihoods. The Arctic is a harbinger of the consequences of multiple global and regional environmental change on ecosystems and livelihoods: The overarching objective of FACE-IT is to enable adaptive co-management of social-ecological fjord systems in the Arctic in the face of rapid cryosphere and biodiversity changes.
Check out this video introduction to FACE-IT: The Changing Arctic Fjord Systems
14
International
institutions
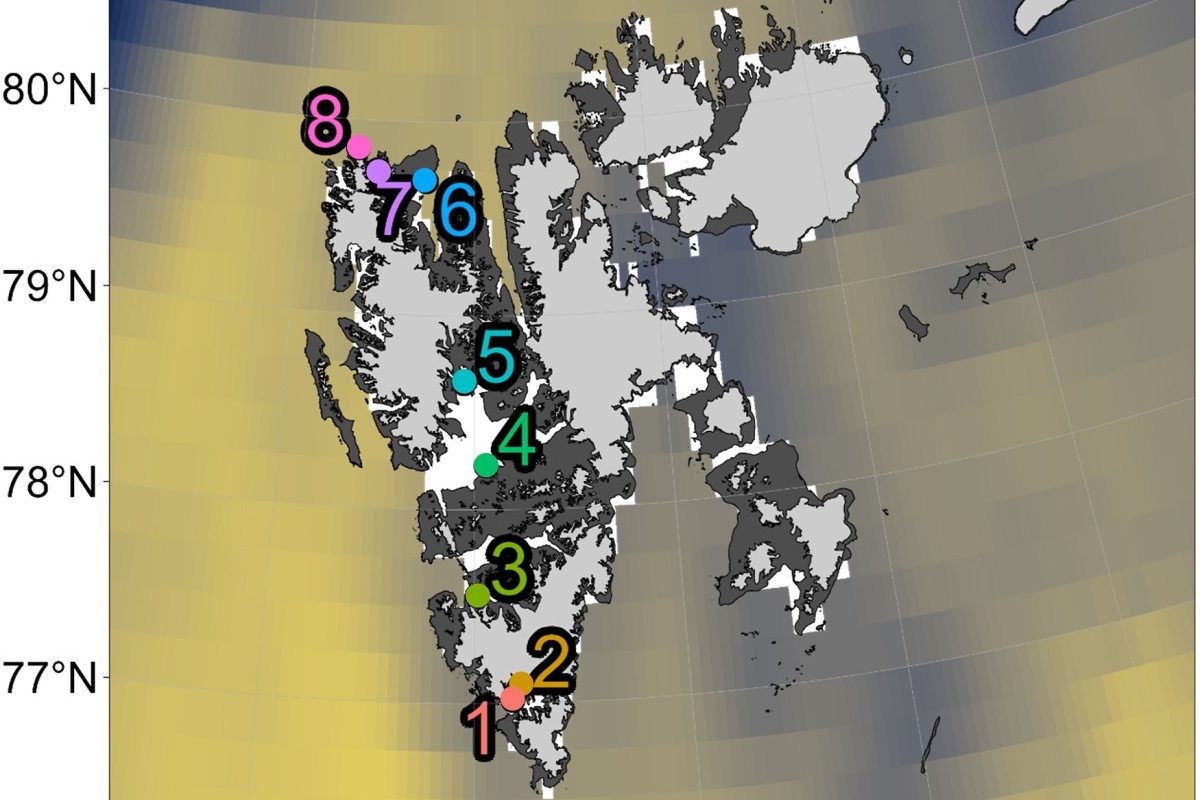
7
Unique
sample sites
8
Countries
Latest Updates
Biodiversity changes in Arctic coastal ecosystems under borealization
January 9, 2026
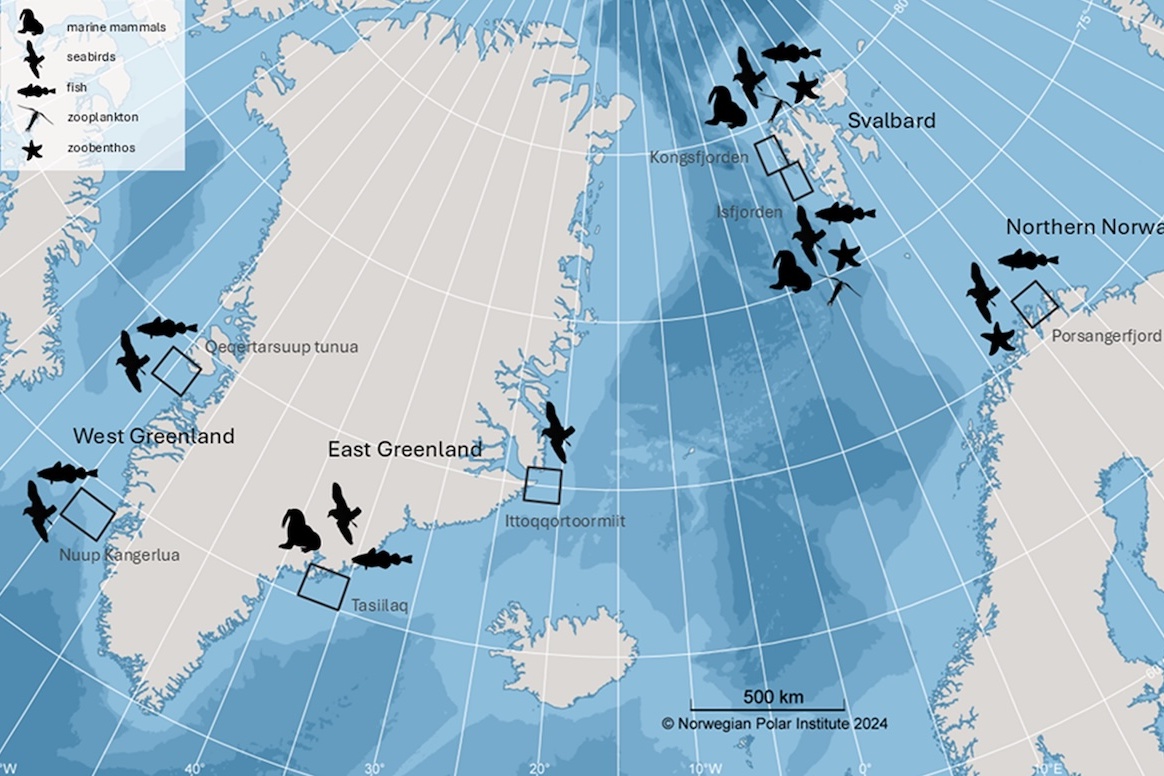
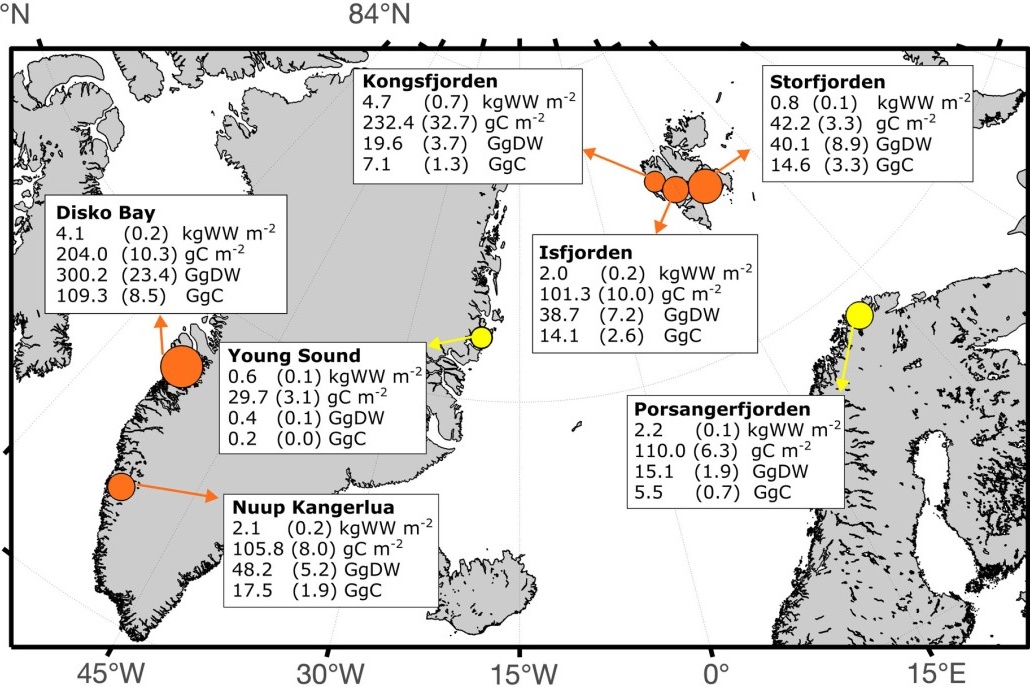
Climate change is playing a major role in the current global biodiversity crisis. However, despite climate change being most pronounced in the Arctic, its impacts on biodiversity in this region remains largely unknown. Here, we combined three decades of abundance data from various animal groups (from zooplankton to megafauna) and regions in the European Arctic and Greenland to assess recent changes in biodiversity within Arctic coastal communities.
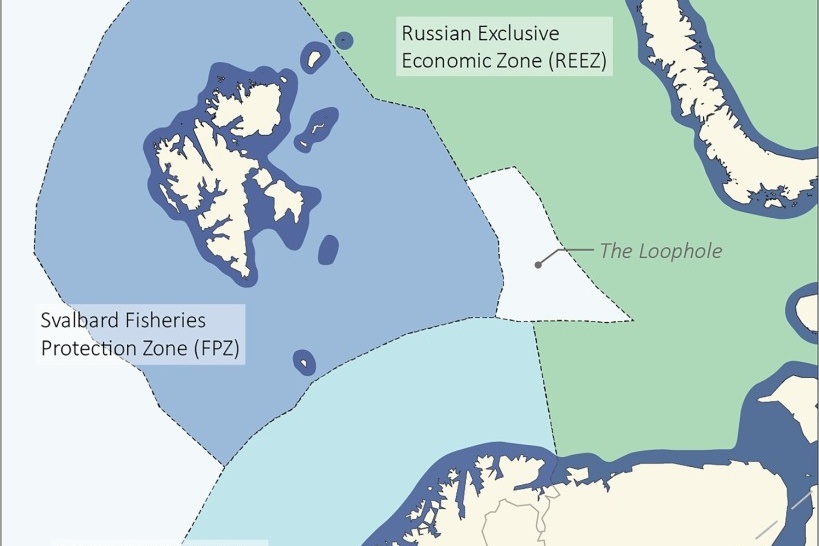
Ongoing changes in distribution of fish species and challenges to fisheries regulations in Isfjorden, Svalbard
December 11, 2025
Changing environmental conditions in Isfjorden impact the abundance and composition of fish species in this major fjord system in Svalbard. New commercially attractive species have already entered and will expand in Svalbard waters. Based on knowledge from different sources, this paper explores and discusses how fisheries may develop in Isfjorden.
Predicting potential Arctic kelp distribution and lower-depth biomass from seafloor irradiance
December 1, 2025
Kelps have an extensive distribution in Arctic coastal waters. However, quantifying their role in the Arctic food web and carbon cycle is challenged by the scarcity of documented geographical distribution, standing stocks and production. Here we present a framework based on an empirical function to predict the potential kelp distribution and their summer biomass as a function of seafloor irradiance and bathymetry.
Klimawandel in der Arktis – ein interdisziplinäres und angewandtes Forschungsbeispiel
November 6, 2025
Die Auswirkungen des Klimawandels manifestieren sich in der Arktis viel schneller als irgendwo sonst auf der Erde. Klimabedingte Veränderungen in Kombination mit lokalen menschlichen Einflüssen belasten die arktischen Ökosysteme schwer. Die daraus folgenden Umweltbedingungen bedrohen auch die Lebensgrundlagen indigener Volksgruppen.
Contested wilderness: The importance of narratives in shaping environmental and tourism governance under a changing climate in Svalbard, Norway
November 6, 2025
Narratives play an important role in shaping conflicts over land use and resource management, as different perceptions of particular places and their desired development are often at the heart of such conflicts. In this study, we examine how a conflict over proposed amendments to regulations on Svalbard can be understood through narratives.
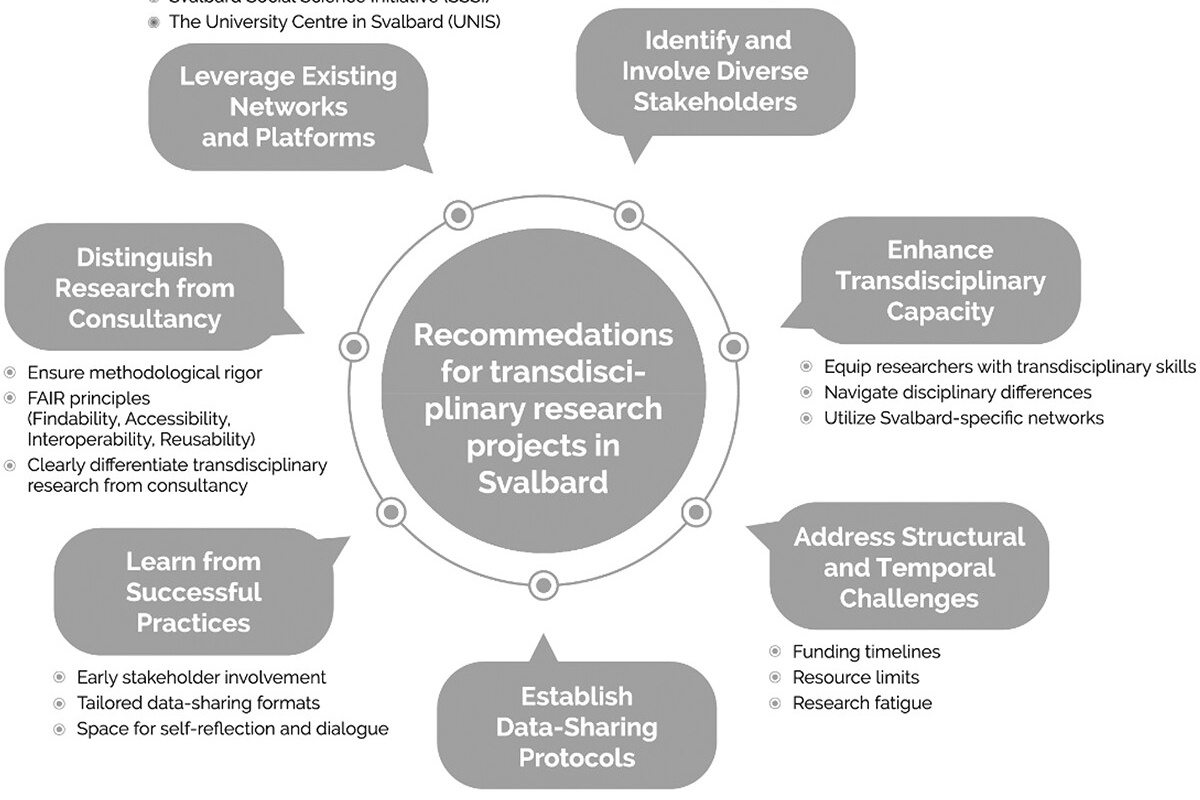
Building transdisciplinary bridges and learning from the Svalbard context
October 31, 2025
This paper explores the challenges and key enablers of transdisciplinary research in the specific context of Svalbard, offering methodological perspectives and recommendations. The interconnected climatic and socioeconomic changes in Svalbard call for collaboration across disciplines, as well as societal stakeholders. Such integrative research collaboration is conceptualised as a transdisciplinary approach.
Biochemistry of Arctic kelp specimens is conditioned by the local environment
October 10, 2025
Climate change causes temperature and light to change drastically in Arctic fjords, being the main drivers for ecosystem-engineering seaweeds (kelps; Laminariales, Phaeophyceae). Climate projections on kelps are often based on static performance curves, treating species as one homogenous unit with similar tolerances within their entire biogeographical range.
Advancing Sustainable Tourism in Svalbard by Assessing and Prioritizing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
October 8, 2025
Tourism is a significant sector on the Svalbard archipelago. The increase in visitors and tourism activities has reshaped the local community of Longyearbyen, brought new economic opportunities, and put greater pressure on the local environment. Tourism operators address ways to integrate the concept of sustainability in their products, management, and communications, as well as focus on selected sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Marie Koch: Sixth PhD thesis defended within FACE-IT
October 6, 2025
On 16 September 2025, Víctor González Triginer successfully defended his PhD thesis, entitled "Ecological transitions in Arctic marine ecosystems - Macroalgal settlement, pelagic density, and fish community shifts associated with glacier retreat and Atlantification". Prior to the defense, Víctor presented a trial lecture with the title “Integrating Underwater Acoustics, Optics, and Artificial Intelligence for Advanced Marine Ecosystem Monitoring”.